PeriCord, a bioimplant for infarcted hearts
 The journal “EBioMedicine” of “The Lancet” has just published the procedure that allowed the creation, last year, of the “PeriCord”, the first human cardiac bioimplant, in which development the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) played a key role.
The journal “EBioMedicine” of “The Lancet” has just published the procedure that allowed the creation, last year, of the “PeriCord”, the first human cardiac bioimplant, in which development the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) played a key role.
In May 2019, a collaboration between the ‘Germans Trias i Pujol’ Hospital, the Blood and Tissue Bank (BST) and IBEC took a step forward for heart patients combining medicine, science and engineering.


 The journal “EBioMedicine” of “The Lancet” has just published the procedure that allowed the creation, last year, of the “PeriCord”, the first human cardiac bioimplant, in which development the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) played a key role.
The journal “EBioMedicine” of “The Lancet” has just published the procedure that allowed the creation, last year, of the “PeriCord”, the first human cardiac bioimplant, in which development the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) played a key role. 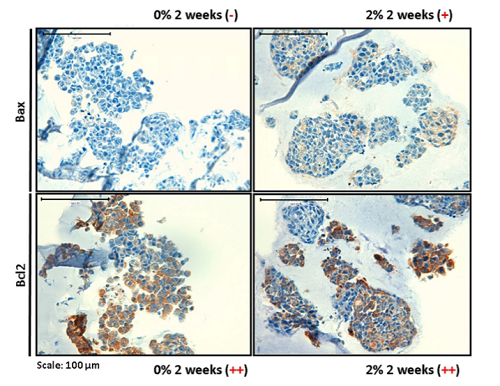
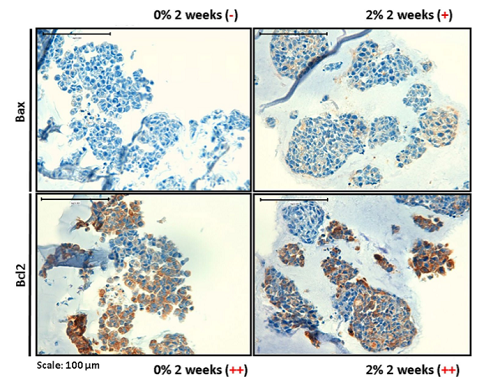 IBEC contributes to elucidate how the rigidity of the tumor extracellular matrix affects the aggressiveness of neuroblastoma, a cancerous tumor that affects mainly children. This opens the door to generate more accurate models to predict tumor development in patients and to work in the design of new treatments.
IBEC contributes to elucidate how the rigidity of the tumor extracellular matrix affects the aggressiveness of neuroblastoma, a cancerous tumor that affects mainly children. This opens the door to generate more accurate models to predict tumor development in patients and to work in the design of new treatments. 
 IBEC researchers led by ICREA Research Professor Núria Montserrat, together with international collaborators, have identified a drug capable of blocking the effects of the SARS-Co-V2 virus, the origin of the Coronavirus 2019 disease.
IBEC researchers led by ICREA Research Professor Núria Montserrat, together with international collaborators, have identified a drug capable of blocking the effects of the SARS-Co-V2 virus, the origin of the Coronavirus 2019 disease.
 Researchers at Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have proposed a model that gives important insights into how nanoparticles interact with cells, virus, bacteria or proteins, among others.
Researchers at Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have proposed a model that gives important insights into how nanoparticles interact with cells, virus, bacteria or proteins, among others. 

 The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
 José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells.
José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells.