About
The Biosensors for bioengineering group is a senior group under ICREA’s Tenure Track scheme.
Organs-on-a-chip (OOC) refers to a technology that involves creating microscale devices that mimic the structure and function of human organs. These “chips” are typically composed of living cells arranged on a microfluidic platform, allowing researchers to simulate the complex interactions and physiological responses within a specific organ.
The goal of Organs-on-a-chip (OOC) technology is to provide a more accurate and representative model of human organs compared to traditional in vitro cell cultures or animal testing. By replicating the microenvironment of organs and incorporating various cell types, organs-on-a-chip can help researchers study the effects of drugs, toxins, and diseases in a more realistic and controlled manner.
Each organ-on-a-chip device is designed to replicate the unique characteristics of a particular organ, such as the liver, pancreas or skeletal muscle. These miniature systems enable researchers to observe and analyze how different substances and conditions affect cellular behavior, tissue function, and overall organ responses. The technology holds promise for drug development, disease modeling, and toxicology studies, offering a more ethical and efficient alternative to traditional methods.
Our research on OOC development has clear goals. We want OOC platforms to be easy to use and more automation to set up cell cultures. This will help more people use them, making experiments quicker and more reliable.
We’re working on creating a simple platform for growing microtissues in 3D. This makes OOC research easier to use in the real world, moving from lab tests to practical applications. We also want to improve the user experience by making OOC platforms more friendly, compatible, and ready for use.
As OOC research moves from labs to real-world use, we want to help users deal with biological challenges. We’re developing an easy-to-use 3D tissue platform and a simple bioreactor that works with sensing technology. This helps users focus on solving biological problems, validating models, and finding potential medicines. We’re also adding sensors to make the bioreactor even more effective.
Our efforts make it easier for researchers to study how organs interact. Our second goal focuses on studying more complex disease models. This helps us understand diseases better and find ways to treat them. We believe that OOCs help in three main ways: understanding diseases, making better medicines faster, and supporting personalized research using cells from individual patients. OOCs can be a solution for studying rare diseases where other methods are not available.
Our third goal is to standardize OOC platforms, making them work together better. This involves creating common rules and standards for everyone to follow. This makes collaboration and sharing information easier.
Finally, our lab is working towards making OOCs suitable for high-throughput screening. This means making them simpler and adding good models for studying diseases. In short, we’re making OOC development more user-friendly, accessible, and technologically advanced. This simplification helps in biological research and finding new medical solutions.
Staff
Javier Ramón Azcón
Projects
| NATIONAL PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Development of a “Muscle-on-a-Chip” (MoC) platform for the preclinical evaluation of potential therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (2020-2022) | DUCHENNE ESPAÑA, IV Convocatoria Ayudas a Proyectos de Investigación | Juanma Fernandez |
| BLAD · BioLiver Assist Device (2020-2021) | AGAUR, Ajuts per a projectes innovadors amb potencial d’incorporació al sector productiu – LLAVOR | Javier Ramón |
| INNOTEC- Javier Ramon- Naturfiltr (2021-2023) | TECNIO | Javier Ramón |
| ASITOC Atomic-Sensor-Integrated Tissue-On-a-Chip: optically detected biomagnetism to understand muscular diseases (2021-2022) | BIST_Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology | Juanma Fernandez |
| INTERNATIONAL PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| DAMOC · ‘Diabetes Approach by Multi-Organ-on-a-Chip’ (2017-2022) | ERC | Javier Ramón |
| BLOC · Benchtop NMR for Lab-on-Chip (2020-2022) | European Comission FET-Open | Javier Ramón |
| PRIVATELY FUNDED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Tatami · Therapeutic targeting of MBNL microRNAs as innovative treatments for myotonic dystrophy (2019-2022) | Fundació bancaria “La Caixa” | Javier Ramón |
| FINISHED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Programa Faster Future 2020: COVID-19 (2021) | Fundraising | Javier Ramón |
| INDUCT · Fabrication of a biomimetic in vitro model of the intestinal tube muscle wall: smooth muscle-on-a-chip (2018-2020) | MINECO | Javier Ramón |
Publications
(See full publication list in ORCID)
[br]
Equipment
Micro and nanofabrication techniques:
- 3D microstructures on hydrogel materials
- Mini-bioreactor for 3D cell culture
- Microelectrodes fabrication
- Synthesis and chemical modification of polymers and surfaces
- Dielectrophoretic cells and micro particles manipulation
Characterization techniques:
- Optical Microscopes (white light/epifluorescence)
- Electrochemical techniques (Potentiometric/Amperometric/Impedance spectroscopy)
- Immunosensing techniques (Fluorescence ELISA/Colorimetric ELISA/magneto ELISA)
Equipment:
- Microfluidic systems (High precision syringe pumps/Peristaltic pumps/Micro valves)
- Biological safety cabinet (class II)
- Epifluorescence microscope for live-cell imaging
- Pulsar – a high-resolution, 60MHz benchtop NMR spectrometer from Oxford Instruments
Access to the Nanotechnology Platform (IBEC Core Facilities): equipment for hot embossing lithography, polymer processing and photolithography, chemical wet etching, e-beam evaporation and surface characterization (TOF-SIMS)
Access to the Scientific and Technological Centers (University of Barcelona): equipment for surface analysis (XPS, AFM, XRD), organic structures characterization (NMR) and microscopy techniques (SEM, TEM, confocal)
Collaborations
We collaborated closely with Professor Ruben Artero from Instituto de Investigaciones Clínicas de Valencia (INCLIVA) and medical doctor Vilchez from Hospital de la Fe (Valencia). We develop muscle-on-a-chip devices using 3D tissue cultures and biosensors. During my career, I established national and international collaborations with other researchers, clinicians, and companies. This is reflected by the fact that I attracted competitive funding awarded by the prestigious entity Medical Research Council (UK), focused on studying Duchenne’s rare disease. I also collaborate on projects with more clinical groups and hospitals, e.g., Hospital de Sant Pau (Barcelona). With senior professor Eduard Gallardo’s group, we are developing human microtissues to study the myasthenia gravis neuromuscular rare disease.
Following the translational nature of my research, I recently became the entrepreneurial scientist of a valorisation project financed by Producte Call (AGAUR) to bring to the market plasmonic biosensors for Myasthenia Gravis diagnosis. I actively collaborate with patient associations such as “Duchenne Parent Project ” and “Asociación Conquistando Escalones,” and with national and international companies such as Arthex biotech, SOM biotech, BI/OND (The Netherlands), and BioEmTech (Greece). I have also established contacts with the industry to develop new technology with a high impact on clinical diagnosis and drug development. Specifically, we collaborate with Grifols (Spain), Multivawe (Switzerland), Oxford Instrument (UK) and NovoNordisk (Denmark). This last collaboration aims to develop new biomaterials for cell therapies. I have also established contacts with the industry to develop new technology with a high impact on clinical diagnosis and drug development, specifically collaborating with Multiwave (Switzerland) and Oxford Instrument (United Kingdom). I am also co-founder of a spin-off company, Vitala.
News

Finançament europeu per al tractament de la diabetis tipus 1 mitjançant bioimpressió 3D
L’investigador de l’IBEC Javier Ramón Azcón ha rebut una “ERC Proof of Concept Grant”. Es tracta d’ un prestigiós finançament que concedeix el Consell Europeu de Recerca per explorar el potencial comercial i social de projectes de recerca duts a terme en institucions europees. El projecte de Ramon, Uniink, s’enfoca en el tractament de la diabetis tipus 1 amb teràpia cel·lular i bioimpressió 3D.

L’investigador de l’IBEC James Eills assistirà a una trobada amb premis Nobel
El Dr. James Eills, investigador de l’IBEC, ha estat seleccionat per assistir al prestigiós Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting que reuneix destacats joves científics d’arreu del món amb premis Nobel. Enguany, … Read more

Cimera científica per lluitar contra les malalties neuromusculars
Científics i pacients es reuneixen a l’IBEC per buscar noves estratègies de tractament per a aquestes patologies minoritàries El diari Ara va entrevistar a Juanma Fernández Costa, investigador postdoctoral del … Read more
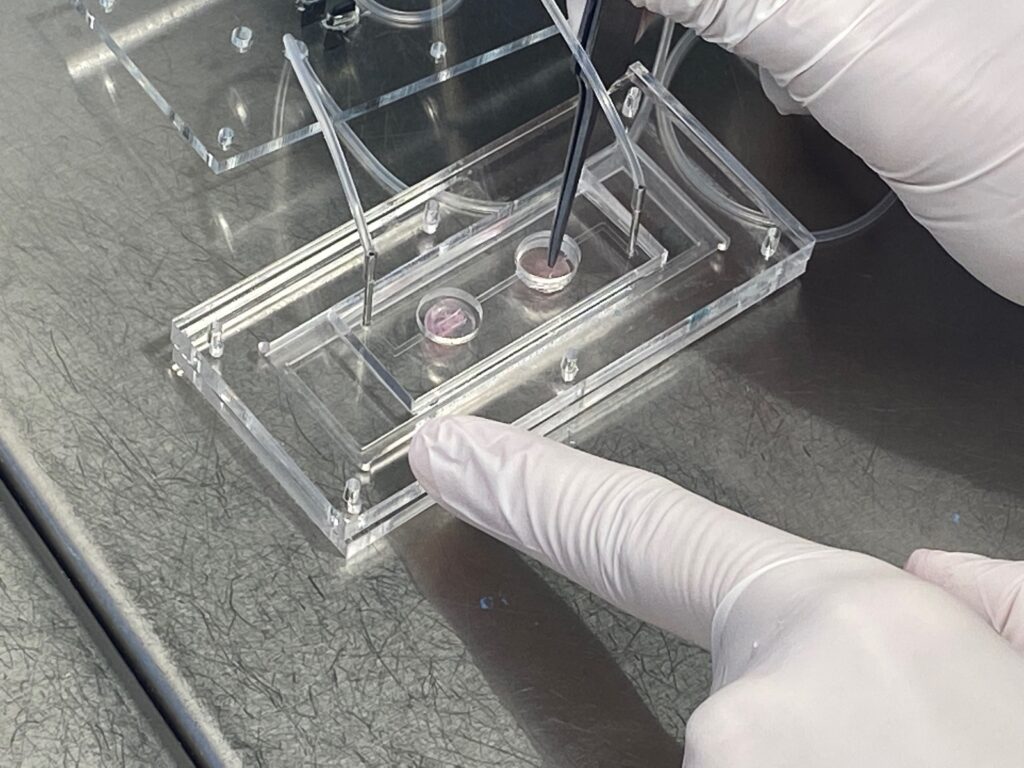

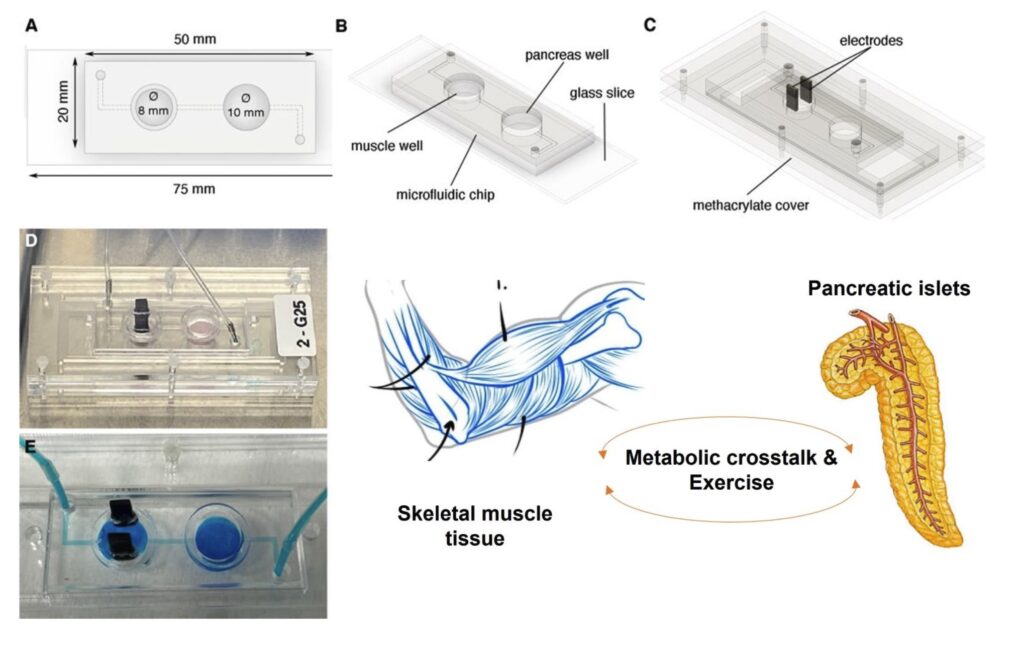
Creen un “gimnàs en un xip” que permetrà estudiar la diabetis i desenvolupar nous fàrmacs per al seu tractament
Coincidint amb el dia mundial de la Diabetis, investigadors de l’IBEC fan públic un estudi en què combinen cèl·lules musculars i de pàncrees en un mateix xip i demostren que … Read more

Bioenginyeria per tractar la diabetis als mitjans
Investigadors de l’Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya (IBEC) liderats pel Professor de Recerca ICREA Javier Ramón, apareixen als mitjans per un recent estudi en col·laboració amb investigadors de l’IDIBAPS, on han desenvolupat petites esferes capaces de respondre a variacions en els nivells de glucosa i produir insulina in vitro.

Innovadores esferes fabricades amb bioenginyeria podrien ajudar contra la diabetis
Investigadors de l’IBEC, en col·laboració amb l’IDIBAPS a Barcelona, han desenvolupat petites esferes capaces de respondre a variacions als nivells de glucosa, i de produir insulina, in vitro. Aquests esferoides biomimètics, i no tòxics, contenen cèl·lules β pancreàtiques i es preparen utilitzant tecnologia de bioimpressió 3D. Aquest enfocament podria ajudar, en el futur, a millorar els resultats clínics de les estratègies de trasplantament de cèl·lules β que es fan servir el tractament de la diabetis, així com per a les plataformes in vitro de desenvolupament de fàrmacs.

Les teràpies regeneratives del futur van confluir al Simposi IBEC, amb experts internacionals i més de 300 inscrits
Més de tres-cents experts internacionals en el camp de la investigació en teràpies regeneratives es van citar al simposi organitzat per l’Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya (IBEC) per presentar els últims avenços en miniòrgans, òrgans-en-un-xip, bioimpressió 3D i enginyeria de teixits, entre d’altres.
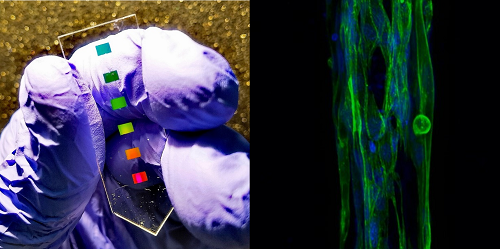
Nou biosensor amb alta sensibilitat detecta marcador inflamatori al múscul
En una publicació recent a la revista Nanophotonics, investigadors de l’IBEC presenten un nou biosensor per a la detecció directa i sensible de la proteïna interleucina-6 al múscul, un indicador d’inflamació i de potencial malaltia, demostrant l’alt rendiment del dispositiu en músculs esquelètics obtinguts per bioenginyeria 3D. Aquest nou enfocament pot resultar en una eina prometedora per mesurar l’eficàcia de fàrmacs davant de malalties en què hi ha inflamació, com la distròfia muscular.

Cap a un tractament per a la distròfia miotònica: primer model 3D amb cèl·lules de pacients
Investigadors de l’IBEC liderats per Javier Ramón i Juan M. Fernández desenvolupen el primer model tridimensional per a la distròfia miotònica, una malaltia rara i sense cura. El model combina cèl·lules de pacient i tècniques de bioenginyeria i representa un gran avenç respecte a la utilització d’animals i de cultius cel·lulars.
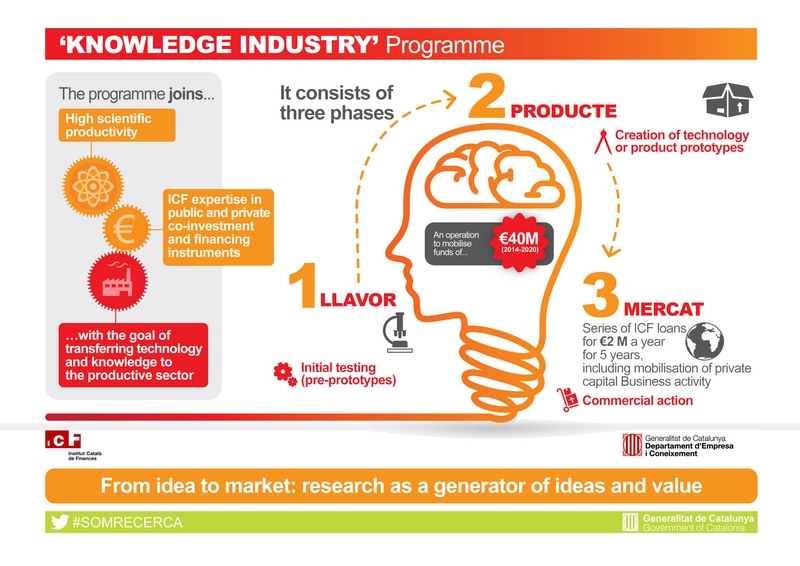
Two IBEC projects granted by “Knowledge Industry Call” of the Catalan Government
A project led by Elisabeth Engel aimed to fabricate and test a dressing prototype for wound healing, and another project led by Javier Ramón with the goal of developing an artificial liver, have been granted by the Knowledge Industry Programme of the Catalan Government.
Jobs
Postdoctoral Researcher at the Biosensors for Bioengineering Research Group
Ref: PR_JR/Deadline: 09/12/2023
Postdoctoral position at the Biosensors for Bioengineering Research Group
Ref: PD_JR/ Deadline: 10/11/2023
Laboratory Assistant at the Biosensors for Bioengineering Research Group
Ref: LA_JR/Deadline: 22/11/2023
Laboratory Technician at the Biosensors for Bioengineering Research Group
Ref: LT_JR//Deadline: 28th April 2023


 ibecbarcelona.eu
ibecbarcelona.eu