- Este evento ha pasado.
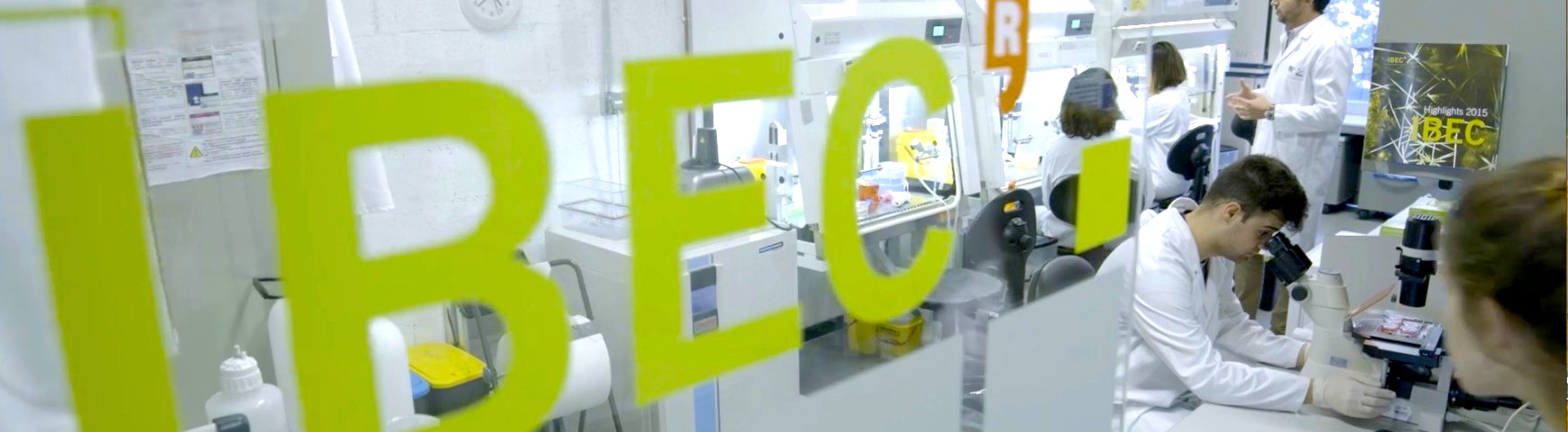
Workshop 2. NET-AI: AI fundamentals and use cases in healthcare
In this second workshop of the AI for Bioengineering thematic network (NET-AI), an introduction, both theoretical and practical, to the fundamental concepts and main algorithms of artificial intelligence applied to bioengineering will be given. To this end, a first seminar will introduce the fundamental concepts of AI. This will be followed by a practical programming activity in Python, in which attendees will be able to bring their laptop to practice the implementation of simple AI models. Finally, a second seminar will offer a more specific vision of AI use cases in the healthcare field for decision-making.
Schedule programme
09:00 – Registration and Welcome
09:15 – Santiago Marco, IBEC group “Signal and Information Processing for Sensing Systems”, “AI fundamentals”
10: 15 – Coffee Break
10:45 – Moritz Marquardt, University of Stuttgart, AI practical activity (own computer required)
12:15 – Short break
12:30 – Plenary: Alexandre Perera, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC),“From Ontology-Based Classifiers for Rare Conditions to Transformer-Based Models for Type 2 Diabetes – Opportunities and Risks”
13:30 – Final remarks and closing
To register, click here.
Health Data Science: From Ontology-Based Classifiers for Rare Conditions to Transformer-Based Models for Type 2 Diabetes – Opportunities and Risks
Alexandre Perera
Health data science is transforming disease prediction and diagnosis through advanced AI models. This talk explores two key frontiers: ontology-based classifiers for rare diseases and transformer-based models for type 2 diabetes prediction. Ontology-based methods, such as those leveraging the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO), enhance diagnostic precision in rare conditions by mapping patient-reported symptoms to expert-curated knowledge bases (Manzini et al., 2022). Initiatives like Share4Rare promote citizen science and collaborative rare disease research, fostering data sharing and patient engagement (Radu et al., 2021). Additionally, expert models aid in the early identification of inherited kidney diseases, integrating clinical expertise with machine learning (Fayos de Arizon et al., 2023) For prevalent conditions like type 2 diabetes, deep learning models excel in trajectory prediction using longitudinal health records. Attention-based encoders and deep clustering approaches have demonstrated high accuracy in forecasting disease progression and personalizing treatment strategies (Manzini et al., 2022, 2025). However, the integration of AI in clinical decision-making presents both opportunities and risks, including model bias, explainability challenges, and ethical concerns regarding data privacy. This discussion highlights the transformative potential of AI-driven disease prediction while addressing the need for robust validation, transparency, and responsible deployment in healthcare.





