Search Results for:
IBEC receives ‘HR Excellence in Research’ award from the European Commission

IBEC has been awarded the ‘Human Resources Excellence in Research’ from the European Commission, in recognition of its commitment to continuously improving its HR policies in line with The European Charter of Researchers and The Code of Conduct for the Recruitment of Researchers (Charter and Code).
IBEC can now use the official HR Excellence in Research logo to help promote itself as a provider of a stimulating and favourable work environment according to the Charter and Code, which describe the rights and responsibilities of researchers and their employers and contribute to the creation of a labour market that is transparent, attractive and open at an international level.
Sant Jordi in the Garden
Please be prompt!
Sant Jordi in the Garden
Please be prompt!
PhD thesis defence: Juan Pablo Agusil
Fabrication of (bio)molecular patterns with contact printing techniques
PhD thesis defence: Juan Pablo Agusil
Fabrication of (bio)molecular patterns with contact printing techniques
IBEC group leader a fem.talent award winner
 IBEC group leader Alicia Casals received a 2015 fem.talent Award at the fem.talent Fòrum in Barcelona on Friday.
IBEC group leader Alicia Casals received a 2015 fem.talent Award at the fem.talent Fòrum in Barcelona on Friday.
Alicia (third from right) won the prize for “Career trajectory”, recognising such milestones as the creation in 2011 of IBEC/UPC spin-off Rob Surgical Systems. Other award categories were “Emerging Talent”, “Innovation” and “Communication”.
The forum is a yearly conference of fem.talent, an initiative of the Network of Science and Technology Parks of Catalonia (XPCAT) that aims to promote equality of opportunity between men and women. This year the theme was “Smart Time: intelligent management of time,” with the objective of discussing innovative ideas and different practices in the field of time management.
Convergència representatives visit IBEC
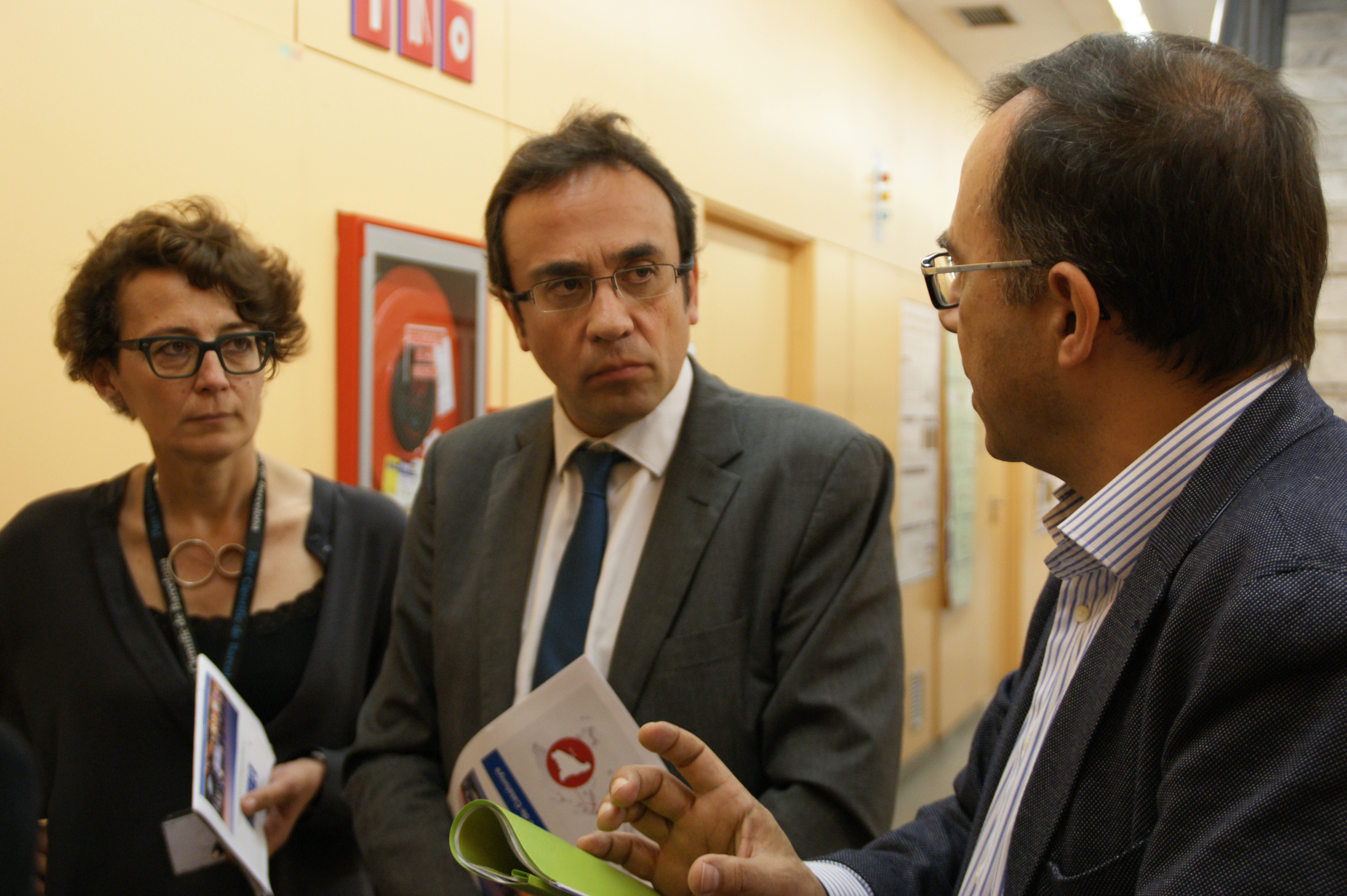
 On Friday morning representatives of Catalan political party Convergència i Unió (CIU) visited IBEC as part of a tour of the PCB.
On Friday morning representatives of Catalan political party Convergència i Unió (CIU) visited IBEC as part of a tour of the PCB.
Congresswoman Imma Riera and organizational secretary Josep Rull met IBEC Director Josep Samitier, who gave them an overview of IBEC, before visiting the Nanotechnology Platform, guided by coordinator Mateu Pla.
reSEARCH4TALENT Open Day
On Thursday 30th April we’ll open our doors to Undergraduate & Masters students interested in a research career.
reSEARCH4TALENT Open Day
On Thursday 30th April we’ll open our doors to Undergraduate & Masters students interested in a research career.

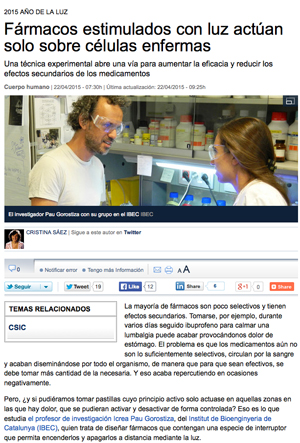



 On Friday morning representatives of Catalan political party Convergència i Unió (CIU) visited IBEC as part of a tour of the PCB.
On Friday morning representatives of Catalan political party Convergència i Unió (CIU) visited IBEC as part of a tour of the PCB.