Possible new treatment for bladder cancer using a mycobacterium
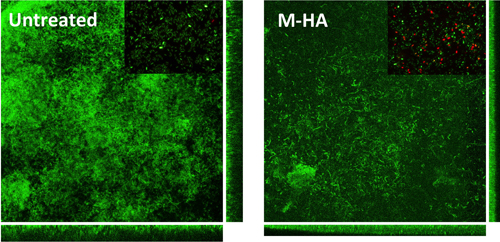
 Collaborators at the UAB and IBEC have found a mycobacterium that is more effective in treating superficial bladder cancer and does not cause infections, unlike those used up to now.
Collaborators at the UAB and IBEC have found a mycobacterium that is more effective in treating superficial bladder cancer and does not cause infections, unlike those used up to now.
Mycobacteria are the only bacteria used in cancer treatment. The administration of the bacterium Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) is the current treatment for superficial bladder cancer, and is inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter. BCG prevents new tumours from appearing, but despite its efficacy it has many adverse side effects, the most serious being BCG infections that need to be treated with antituberculous drugs.

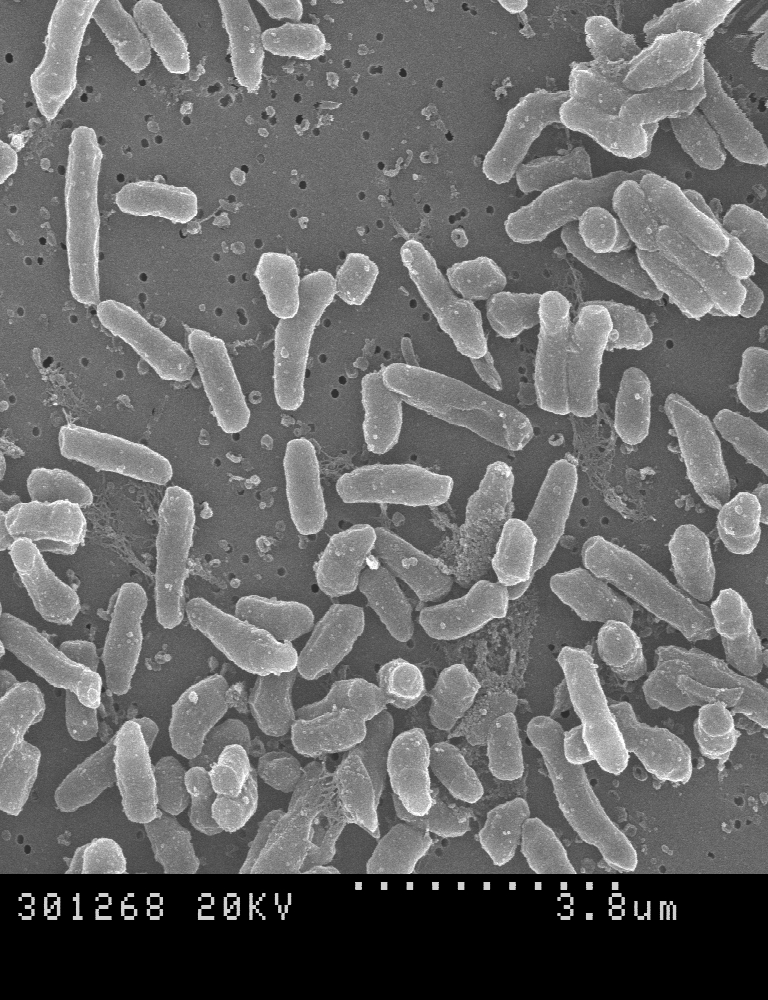
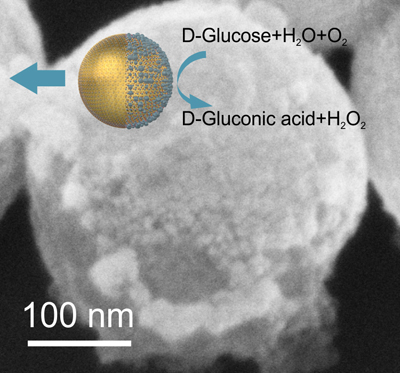
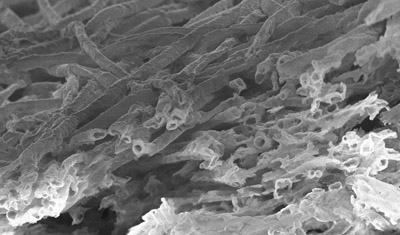

 Researchers at the Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, the Hospital Sant Joan de Deu and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study, led by Dr. Juan Carlos Izpisúa Belmonte of the Gene Expression Laboratory at California’s Salk Institute, that uses molecular “scissors” to remove mitochondrial mutations in mouse eggs.
Researchers at the Hospital Clínic, IDIBAPS, the Hospital Sant Joan de Deu and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study, led by Dr. Juan Carlos Izpisúa Belmonte of the Gene Expression Laboratory at California’s Salk Institute, that uses molecular “scissors” to remove mitochondrial mutations in mouse eggs. 
 Pioneering international study supported by the Obra Social “la Caixa” opens new possibilities to control metastasis
Pioneering international study supported by the Obra Social “la Caixa” opens new possibilities to control metastasis