Scientists map the first step in Alzheimer’s protein aggregation and discover clues for future therapies
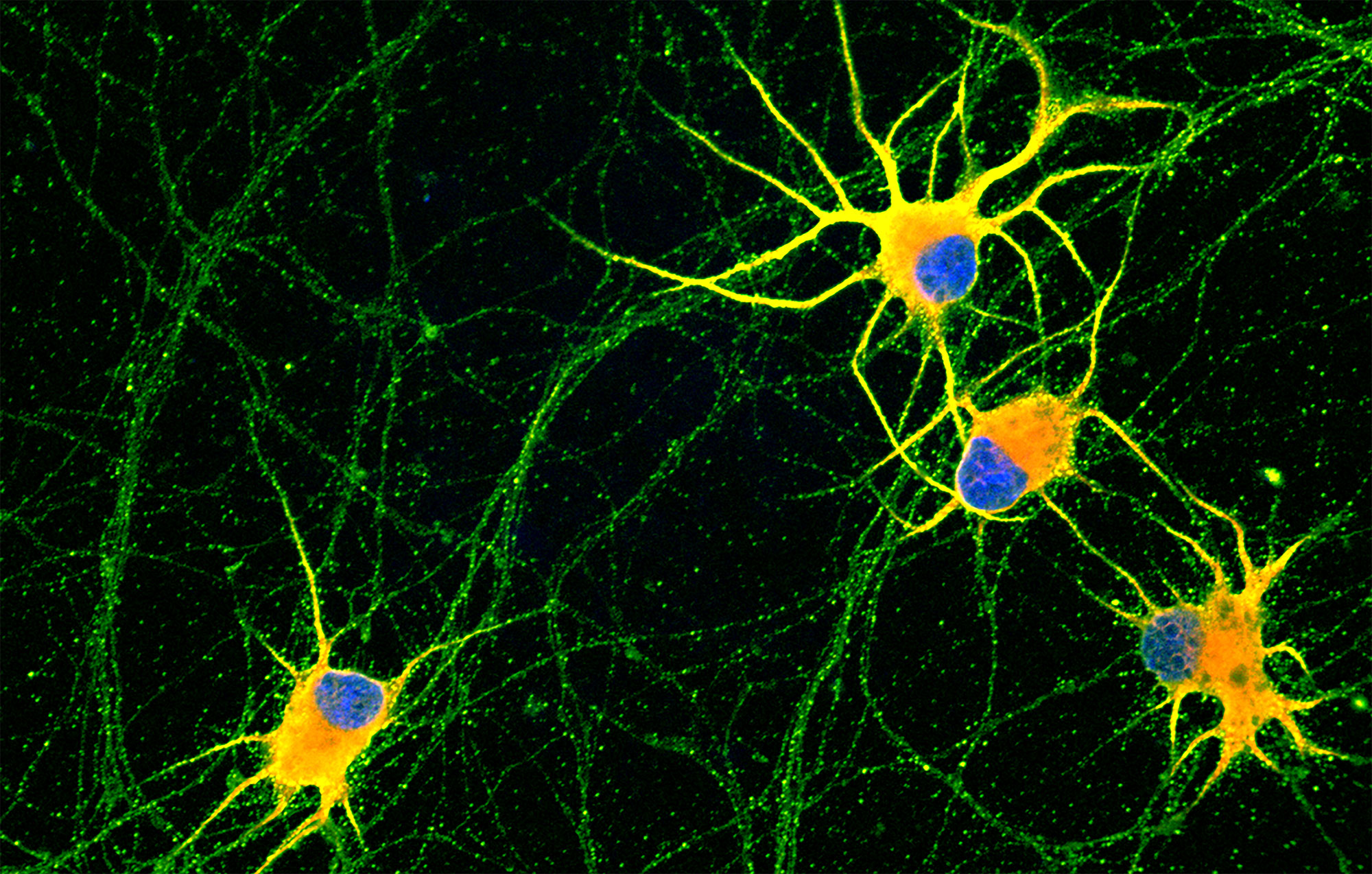
This is an analysis on an unprecedented scale. They studied over 140,000 versions of the Aβ42 peptide, which forms harmful plaques in the brain. It is the first map to reveal how mutations affect a protein in its transition state — a fleeting phase that is difficult to study. This finding opens up new avenues for preventing Alzheimer’s disease and suggests a method that can be applied to studying other proteins involved in different pathologies. The study, published in Science Advances, is a collaboration between the Wellcome Sanger Institute in the United Kingdom, the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia, and the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona.