ERC President visits IBEC
The President of the European Research Council, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, visited last May 15th the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC).
The event was inaugurated by IBEC’s Director, Josep Samitier, who presented an overview on the cutting-edge research carried out at the institute in the fields of bioengineering and nanomedicine.
Afterwards, ERC Grantees working at IBEC had the opportunity to explain the impact of ERC grants on their professional careers and established a dialogue with ERC President on the past, present and future of the European Research Council.


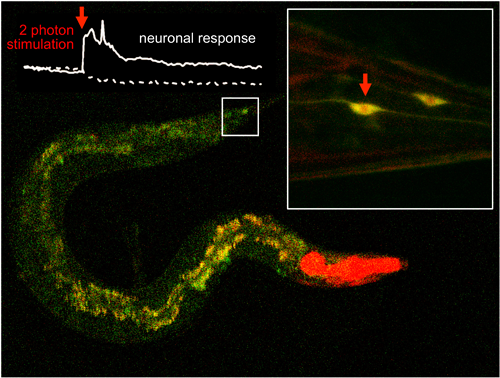
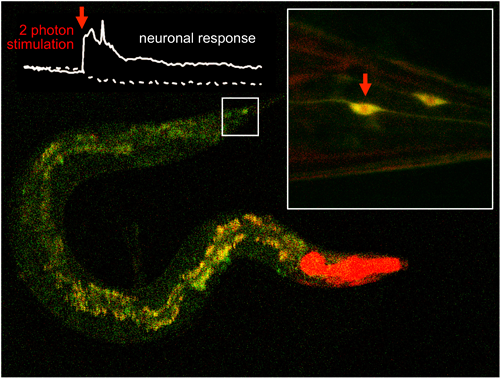 A scientific team led by IBEC and UAB manages to efficiently activate molecules located inside cell tissues using two-photon excitation of with infrared light lasers. The results of the study has been published in Nature Communications.
A scientific team led by IBEC and UAB manages to efficiently activate molecules located inside cell tissues using two-photon excitation of with infrared light lasers. The results of the study has been published in Nature Communications.
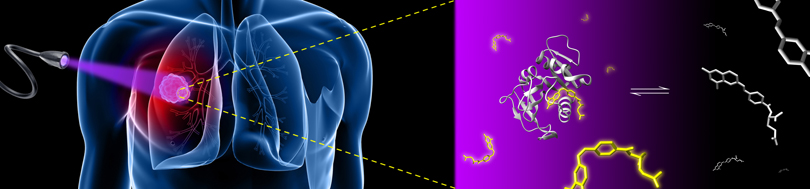
 Collaborating IBEC groups have published a study in Nature Communications that reveals that electron transfer can take place while a protein is approaching its partner site, and not only when the proteins are engaged, as was previously thought.
Collaborating IBEC groups have published a study in Nature Communications that reveals that electron transfer can take place while a protein is approaching its partner site, and not only when the proteins are engaged, as was previously thought. 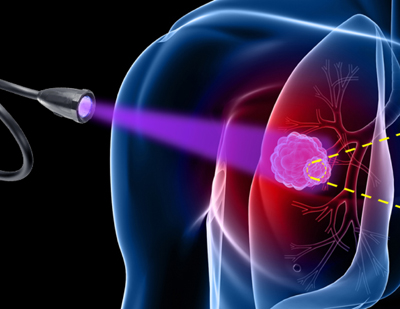
 Researchers at IBEC and IDIBELL have developed a light-regulated molecule that could improve chemotherapy treatments by controlling the activity of anticancer agents.
Researchers at IBEC and IDIBELL have developed a light-regulated molecule that could improve chemotherapy treatments by controlling the activity of anticancer agents.