About
The generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), especially the generation of patient-derived pluripotent stem cells suitable for disease modelling in vitro, opens the door for the potential translation of stem-cell related studies into the clinic.
Successful replacement, or augmentation, of the function of damaged cells by patient derived differentiated stem cells would provide a novel cell-based therapy for diseases. Since iPSCs resemble human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) in their ability to generate cells of three germ layers, patient-specific iPSCs offer definitive solutions for the ethical and histo-incompatibility issues related to hESCs. Indeed human iPSC (hiPSC)-based autologous transplantation is heralded as the future of regenerative medicine.
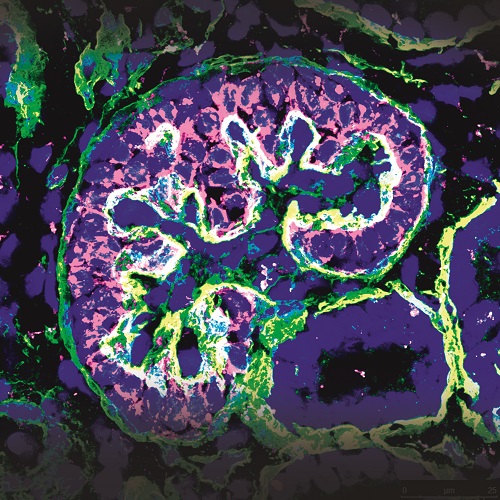
One of our aims is to generate and correct disease-specific hiPSCs for disease modelling and drug screening. The combination of gene-editing based methodologies together with the development of novel protocols for cell differentiation into relevant tissues/organs, provides a unique scenario for modelling disease progression, and the identification of molecular and cellular mechanisms leading to organ regeneration (Figure 1). In this regard we are particularly interested in generation of transgene-free and disease free patient derived hiPSCs for disease modelling and the discovery of novel therapeutic targets.
We believe that the recovery of tissue function should not be restricted to the development of cell replacement therapies. In this regard, in our laboratory we take advantage of organisms that possess the ability to regenerate such as zebrafish, in order to understand which molecular and cellular pathways lead to organ regeneration.
Surprisingly, studies in neonatal mice have demonstrated that soon after birth this organism posses the capability to regenerate its heart. Taking advantage of such preliminary observations we are translating such analysis in order to understand if the mammalian neonatal kidney still posses the capability to regenerate, and more importantly, if we are able to dissect the epigenetic and cellular mechanisms leading to those responses.
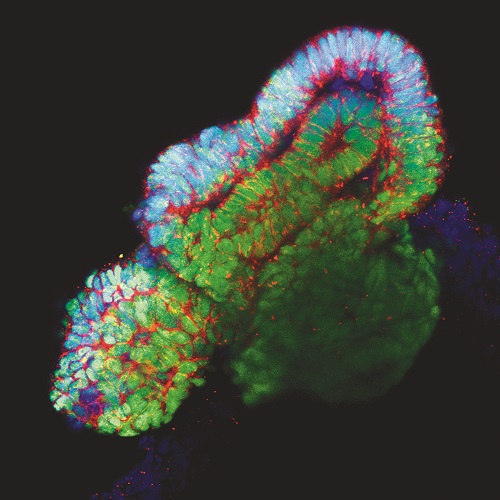
Lastly, and in an effort to fully develop in vitro and ex vivo platforms for organ regeneration, in our lab we are focused in the development of reporter cell lines for different transcription factors essential for tissue-specific commitment and differentiation (i.e: renal and cardiac lineages). The possibility to combine pluripotent stem cell lines together with decellularized matrices, functionalized biomaterials and ex vivo organoids offers and unprecedented opportunity for the immediate generation of patient-specific in vitro and ex vivo platforms for disease modelling and organ regeneration (Figure 2).
Staff
Projects
| NATIONAL PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Bioengeniería para mejorar la salud mediante de organoides y bioimpresión 3D (2021-2023) | MINECO – Plataformas ISCIII de apoyo a la I+D+I en Biomedicina y Ciencias de la Salud | Núria Montserrat |
| CARDIOPRINT Biofabricación avanzada multifunción en 3D para la generación de tejido cardiaco terapéutico a escala humana diseñado por ordenador (2021-2024) | MICIU, Proyectos de I+D+i en líneas estratégicas | Núria Montserrat |
| CAKUTORG Desarrollando nuevas estrategias para entender y tratar las anomalías congénitas del riñón y del tracto urinario mediante organoides (2021-2024) | MICIU, Retos investigación: Proyectos I+D | Núria Montserrat |
| Identifying SARS-CoV-2- host cell interactions exploiting CRISPR/Cas9 engineered human organoids: through the development of specific therapies against COVID19 (2020-2022) | FBBVA | Núria Montserrat |
| CHONDREG · Identification of the epigenetic mechanisms preventing chondrocyte de-differentiation: generation of novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cartilage chronic osteochondral lesions | CIBER | Nuria Montserrat |
| Infarto de miocardio en jóvenes. Factores epigeneticos y nuevos marcadores de riesgo cardiovascular. Efecto de la modulación de la expresión de microRNAs y long-non coding RNAs | ISCIII | (Collaborator) |
| INTERNATIONAL FUNDED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| ENGIORG Engineering kidney organoids to study the interplay between Tissue Mechanics and Metabolism: from development to disease (2021-2026) | European Commission | Núria Montserrat |
| ECaBox ECaBox “Eyes in a Care Box”: Regenerating human retina from resuscitated cadaveric eyes (2021-2025) | European Commission, FET OPEN | Núria Montserrat |
| Engineering functional human kidneys and urinary tracts (2021-2024) | Wellcome Leap Solicitation for Humans Organs, Physiology and Engineering (HOPE) | Núria Montserrat |
| BRAV3. Computational biomechanics and bioengineering 3D printing to develop a personalized regenerative biological ventricular assist device to provide lasting functional support to damaged hearts (2020-2024) | European Commission | Núria Montserrat |
| MAD-CoV 2 · Modern approaches for developing antivirals against SARS-CoV 2 (2020-2024) | European Commission | Núria Montserrat |
| R2U-Tox-Assay · Ready-to-use Toxicity Screening Assay based on iPS-Technologies (2020-2022) | EIT Health | Núria Montserrat |
| PRIVATELY FUNDED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| SYSTORG Exploiting organoid model systems to explore systemic conditions worsening COVID19: merging cellular and genetic engineering (2021-2024) | Fundació La Marató de TV3, TV3-Projectes de recerca La Marató TV3 | Núria Montserrat |
| Identificació de noves dianes terapèutiques i biomarcadors de progressió del càncer de ronyó a través de models organoides i xenoempelts genèticament dissenyats per CRISPR (2020-2023) | Fundació La Marató de TV3, TV3-Projectes de recerca La Marató TV3 | Núria Montserrat |
| REPIRE · Regenerating photoreceptors in human retinal organoids to establish a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa (2018-2021) | Fundación Bancaria “La Caixa” | Núria Montserrat |
| FUNDRAISING PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Programa Faster Future 2020: COVID-19 (2021) | Fundraising | Núria Montserrat |
| FINISHED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Identification of Kidney Cancer progression targets and biomarkers through CRISPR-engineered organoids and xenograft mouse models (2019-2020) | Fundació La Marató de TV3 | Núria Montserrat |
| Generation of Isogenic Models of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) using CRISPR-engineered Kidney Organoids, for the identification of diagnostic biomarkers (2017-2021) | Fundación AECC | Núria Montserrat |
| EPIORG · Cómo modelar la Nefropatía Diabética: restableciendo el epigenoma en organoides renales diabéticos inducidos (2018-2020) | MINECO, Retos investigación: Proyectos I+D | Núria Montserrat |
| MECHANORG · Como integrar señales mecánicas y metabólicas en organoides renales para el modelado de patologías humanas (2019-2020) | MINECO, Acciones Dinamización Europa Investigación | Núria Montserrat |
| Modelling Diabetic Nephropathy targeting DNA methylation: engineering the epigenome in kidney (2019-2020) | EFSD European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes | Núria Montserrat |
| REGMAMKID · How to regenerate the mammalian kidney (2015-2021) | European Commission, ERC-StG | Núria Montserrat |
| REPROMICRO · Reprogramacion y regeneracion tisular a partir de microvesiculas derivadas de celulas madre de pluripotencia inducida (2017-2019) | Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Explora Ciencia | Nuria Montserrat |
| Desarrollo de nuevas estrategias para el tratamiento de la enfermedad renal (2015-2017) | MINECO | Nuria Montserrat |
| TRATENFREN · Desarrollo de nuevas estrategias para el tratamiento de la enfermedad renal (2015-2017) | MINECO, Retos investigación: Proyectos I+D | Nuria Montserrat |
| Regenerative medicine for Fanconi anemia: generation of disease-free patient-specific iPS (2013-2016) | Fundació La Marató de TV3 | Nuria Montserrat |
| ACE2-ORG · Development of a human cellular plaform unveilling Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) – sars-CoV-2 interactions (2020-2021) | ISCIII | Núria Montserrat |
| Red TERCEL · Red de Terapia Celular (2017-2021) | MINECO, ISCIII | (Collaborator) |
| EPIORGABOLISM Diabetic nephropathy modelling in hESC-derived 3D (2019-2021) | European Commission, MARIE CURIE – IF | Carmen Hurtado |
Publications
Equipment
- Real Time QuantStudio 5
- SimpliAmp thermocycler
- Eppendorf 5415D centrifuge
- Allegra X-15 R centrifuge
- Gyrozen 1248 centrifuge
- BioUltra 6 Telstar culture Hood 2x
- AH-100 Telstar primary culture Hood
- Binder CB 60 incubators 2x
- Controltecnica ASTEC SCA 165 incubator
- Controltecnica ZC 180 incubator
- Bioruptor Pico sonicator
- Thermomixer C thermal block
- Leica DMS1000 and DMIL Led microscopes
- Leica DMi1 microscope
- Leica MZ 10F magnifying glass
- Safe Imager 2.0 transilluminator
Collaborations
- Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte
Salk Institute for Biological Studies - Dr. Josep Maria Campistol Plana
Experimental Laboratory of Nephrology and Transplantation, Hospital Clínic, Barcelona - Peter Hohestein
The Roslin Institute, University of Edinburgh - Dr. Pere Gascón Vilaplana
Head of Oncology Service/Molecular and Translational Oncology Laboratory, IDIBAPS - Gloria Calderon
Embryotools SL - Pura Muñoz Cánovas
Departament de Ciències Experimentals i de la Salut, Universitat Pompeu Fabra - Dr. Pedro Guillén
Director Clínica Cemtro, Madrid - Dr. Francisco Fernández Avilés
Head of Cardiology Service, Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid - Dr María Eugenia Fernández
Unit of Cell Production, Hospital Gregorio Marañón, Madrid - Joaquin Gutiérrez Fruitós
University of Barcelona - Dr. Pere Roca-Cusachs
IBEC - Dr. Elena Martínez
IBEC - Dr. Cristina Eguizabal Argaiz
Centro Vasco de Transfusion y Tejidos Humanos (CVTTH), Bizkaia - Dr. Antonio Alcaraz
Head of Urology, Hospital Clínic, Barcelona - Dr. Oriol Casanovas
Head of Tumour Angiogenesis Group, IDIBELL
News

IBEC receives a visit from the Mayor of Barcelona interested in our research against Covid19
The Mayor of Barcelona, Ada Colau, visited IBEC facilities last Friday to learn, by our Director and a group of researchers, how bioengineering can help find solutions to health problems such as COVID19, cancer, or degenerative diseases. When in early 2020, more than 200 scientists gathered in La Pedrera in Barcelona to discuss the present and future of bioengineering, no one imagined that the world would experience the first pandemic of the 21st century and that science would take on more importance than ever.

IBEC receives funding from Carlos III Health Institute to fight COVID-19 using bioengineering
The COVID-19 Fund managed by the Carlos III Health Institute has awarded more than 300,000 euros to the “ACE2-ORG” project led by ICREA research professor Núria Montserrat at IBEC. The resources are intended to study COVID-19 and specify new therapeutic approaches against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona and the University of Navarra also participate in this project.

Núria Montserrat in a feature article at the ERC’s covid-19 section: Stopping coronavirus at the gate
ERC grantee Nuria Montserrat and her team create tiny kidneys which are proving to be key in the search for coronavirus drugs. The researcher is working with other international researchers and found that a trial drug could block early stages of COVID19. The ERC has created a section which is updated with the latest news about the ERC-funded research in coronavirus.
The research with organoids against COVID19 reaches the international press
One of the most prestigious German newspapers, the Süddeutsche Zeitung echoes the work of Núria Montserrat and her international partners who are investigating with organoids a drug that blocks the entrance door of Covid19.

Mini-kidneys to test a drug to stop Covid-19
Nuria Montserrat, principal investigator of the “Pluripotency for organ regeneration” and her group have participated in an international study to find a treatment to stop the virus from continuing infecting other cells, preventing the virus from replicating.

Researchers at IBEC help identifying a drug in clinical phase that blocks the effects of SARS-Co-V2
IBEC researchers led by ICREA Research Professor Núria Montserrat, together with international collaborators, have identified a drug capable of blocking the effects of the SARS-Co-V2 virus, the origin of the Coronavirus 2019 disease. The treatment, which can be tested on two hundred Covid-19 patients as of today, has proven effective in mini-kidneys generated from human stem cells. Using hese organoids generated by bioengineering techniques, it has been deciphered how SARS-Co-V2 interacts and infects human kidney cells.

IBEC researchers contribute to an international study to regenerate infarcted hearts
Within the EU project BRAVƎ, experts at Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) combine cell therapy and bioengineering to design a biological device that recovers cardiac functionality in people with cardiovascular diseases. Researchers at IBEC led by the ICREA Professor Núria Montserrat contribute to the EU project BRAVƎ, an initiative for cardiac regeneration that combines cell therapy and bioengineering to design a biological device capable of recovering cardiac functionality in people with coronary heart disease.

IBEC participates in an international study to stop coronavirus contagion
Researchers at the Institute of Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) led by Professor ICREA Núria Montserrat are studying the role of the receptor ‘Angiotensin converting enzyme’ (ACE2), one of the pathways that the SARS-Co-V2 virus uses to enter our body. To do this, experts use mini-kidneys, as well as other cell cultures such as cardiac organoids. The goal is to exploit these mini-organs to better understand how the virus works.
Núria Montserrat on TV talks about Covid-19
Nuria Montserrat, principal investigator of the “Pluripotency for organ regeneration” spoke today at Espejo Público about the research that her group is carrying out in collaboration with other international research groups to find a treatment to stop the virus from continuing infecting other cells, preventing the virus from replicating.

IBEC joins the BASE3D community to contribute to the future of 3D printing
The Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) will contribute its extensive experience in 3D printing and bioprinting to the BASE 3D community, an entity that brings together research centers and companies from all over Catalonia with the aim of promoting R+D+i in the field of printing 3D. The groups led by Josep Samitier, Elisabeth Engel, Núria Montserrat and Javier Ramón at IBEC are joining the BASE3D project.

