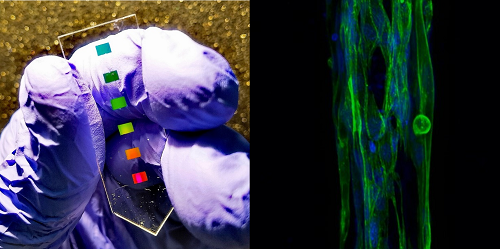
Fibrosens Project receives funds from AFM-Telethon to develop sensor devices for muscular dystrophy
IBEC researcher Juanma Fernández recently has received funding from the French AFM-Telethon to carry out the project “Monitoring of fibrotic processes in 3D skeletal muscle co-cultures for Muscular Dystrophies using plasmonic biosensors”. The objective is to develop multiplexing sensor devices to achieve online, real-time sensing capability to monitor fibrosis markers and evaluate drug response in muscular dystrophy in vitro models.