Nature Physics’ ‘Insight’ issue features IBEC/Crick article
 A review by IBEC group leader and ICREA research professor Xavier Trepat is one of six featured in Nature Physics’ latest ‘Insight’ issue, ‘The Physics of Living Systems’, in which all the articles have been co-authored by a physicist and a biologist.
A review by IBEC group leader and ICREA research professor Xavier Trepat is one of six featured in Nature Physics’ latest ‘Insight’ issue, ‘The Physics of Living Systems’, in which all the articles have been co-authored by a physicist and a biologist.
Penned together with collaborator Erik Sahai from London’s Francis Crick Institute, Xavier’s article, ‘Mesoscale physical principles of collective cell organization’, reviews recent evidence showing that cell and tissue dynamics are governed by mesoscale physical principles – force, density, shape, adhesion and self-propulsion.


 A review by IBEC group leader and ICREA research professor Xavier Trepat is one of six featured in Nature Physics’ latest ‘Insight’ issue, ‘The Physics of Living Systems’, in which all the articles have been co-authored by a physicist and a biologist.
A review by IBEC group leader and ICREA research professor Xavier Trepat is one of six featured in Nature Physics’ latest ‘Insight’ issue, ‘The Physics of Living Systems’, in which all the articles have been co-authored by a physicist and a biologist.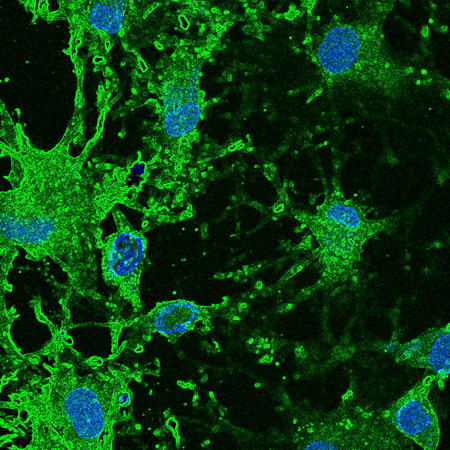
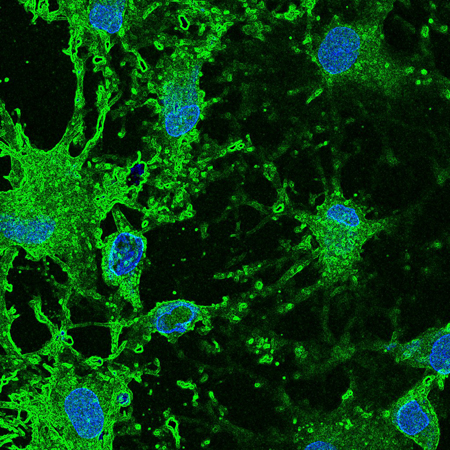 IBEC’s Biomaterials for Regenerative Therapies group has published a review of the state-of-the-art in biomaterials for skin healing that proposes a move towards more personalized, in situ therapies.
IBEC’s Biomaterials for Regenerative Therapies group has published a review of the state-of-the-art in biomaterials for skin healing that proposes a move towards more personalized, in situ therapies.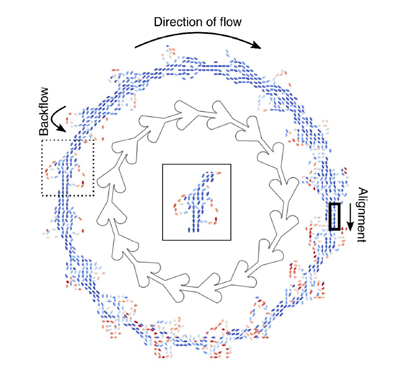
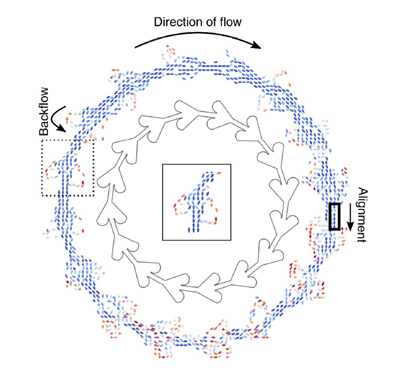 IBEC’s Smart-Nano-Bio-Devices and Nanobioengineering groups have joined forces to solve the problem of random movement of micro- and nanomotors.
IBEC’s Smart-Nano-Bio-Devices and Nanobioengineering groups have joined forces to solve the problem of random movement of micro- and nanomotors.
 Research led by the University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute, with the collaboration with IBEC, reveals that water that’s only a few molecules thick – like the water that covers every surface around us – behaves very differently to normal, ‘bulk’ water.
Research led by the University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute, with the collaboration with IBEC, reveals that water that’s only a few molecules thick – like the water that covers every surface around us – behaves very differently to normal, ‘bulk’ water.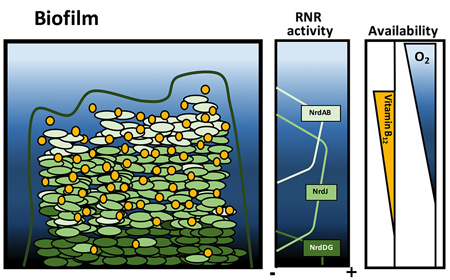
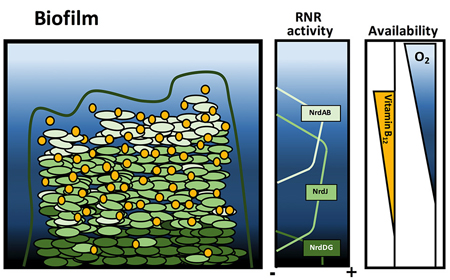 IBEC’s Bacterial infections: antimicrobial therapies group has revealed the essential role played by a vitamin in the development of a common bacterial biofilm.
IBEC’s Bacterial infections: antimicrobial therapies group has revealed the essential role played by a vitamin in the development of a common bacterial biofilm. 
 Researchers at IBEC have discovered that cell division in epithelial tissues is regulated by mechanical forces.
Researchers at IBEC have discovered that cell division in epithelial tissues is regulated by mechanical forces. 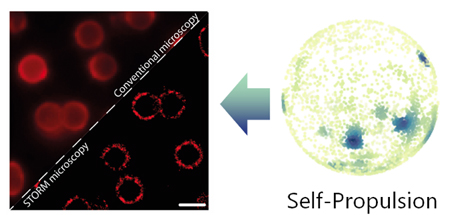
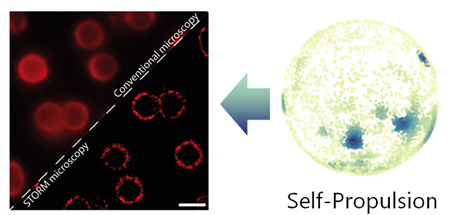 Two IBEC groups have clubbed together to combine their expertise and reveal new knowledge that could advance the design of micro- and nanomotors for applications in health.
Two IBEC groups have clubbed together to combine their expertise and reveal new knowledge that could advance the design of micro- and nanomotors for applications in health.
 Alberto Elosegui-Artola, Xavier Trepat and Pere Roca-Cusachs’ paper in Trends in Cell Biology has made the cover of the latest issue of the Cell-family journal.
Alberto Elosegui-Artola, Xavier Trepat and Pere Roca-Cusachs’ paper in Trends in Cell Biology has made the cover of the latest issue of the Cell-family journal.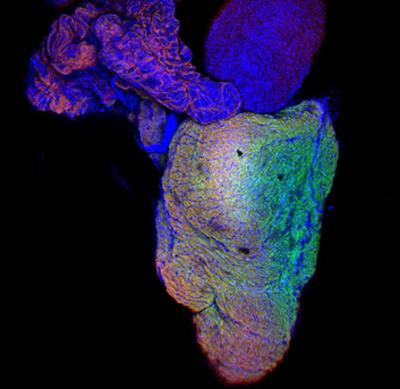
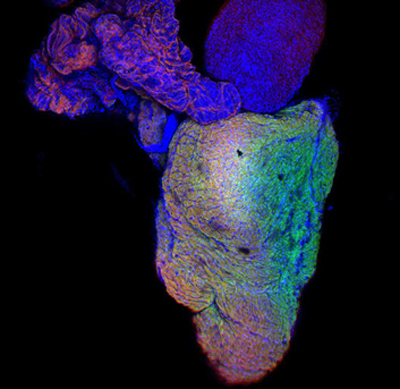 A study carried out at CMR[B] in collaboration with IBEC and the UB has established that the ability of the heart to regenerate after a wound is related to the stiffness of its cellular environment and not only to the proliferative capacity of the cardiac cells, narrowing the window of regeneration to 48 hours after birth.
A study carried out at CMR[B] in collaboration with IBEC and the UB has established that the ability of the heart to regenerate after a wound is related to the stiffness of its cellular environment and not only to the proliferative capacity of the cardiac cells, narrowing the window of regeneration to 48 hours after birth.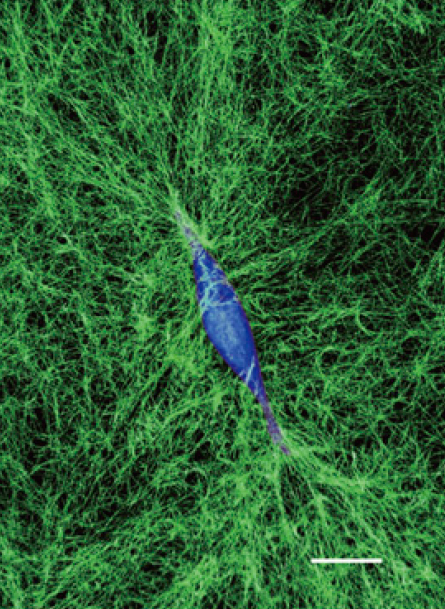
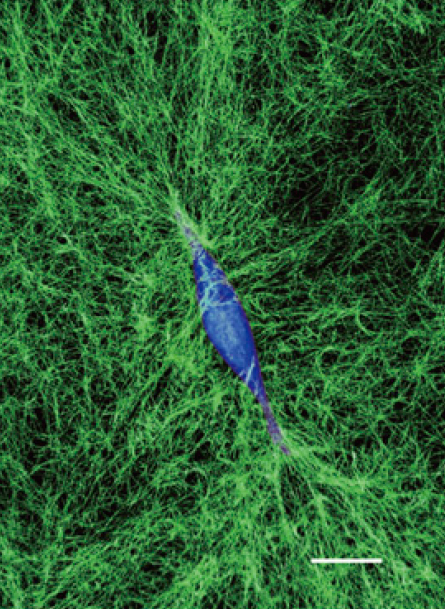 Researchers at IBEC and MIT have shown that cells could use their environment to mechanically communicate with each other within tissues. It’s a bit like when an army cadet pulls some rope netting taut so that his friend can safely ascend.
Researchers at IBEC and MIT have shown that cells could use their environment to mechanically communicate with each other within tissues. It’s a bit like when an army cadet pulls some rope netting taut so that his friend can safely ascend.