About
The Bacterial infections: antimicrobial therapies group is a senior group.
Infectious diseases constitute a tenacious and major public health problem all over the world. The emergence and increasing prevalence of bacterial strains that are resistant to available antibiotics demand the discovery of new therapeutic approaches.
Biofilms are bacterial communities that grow embedded within a protective matrix produced by themselves.
Chronic infections caused by bacteria growing in biofilms, are enormously complicated to treat. It increases their fitness and survival, thus complicating treatment and diagnosis because they persist despite the action of antibiotic therapies and adaptive immune responses.
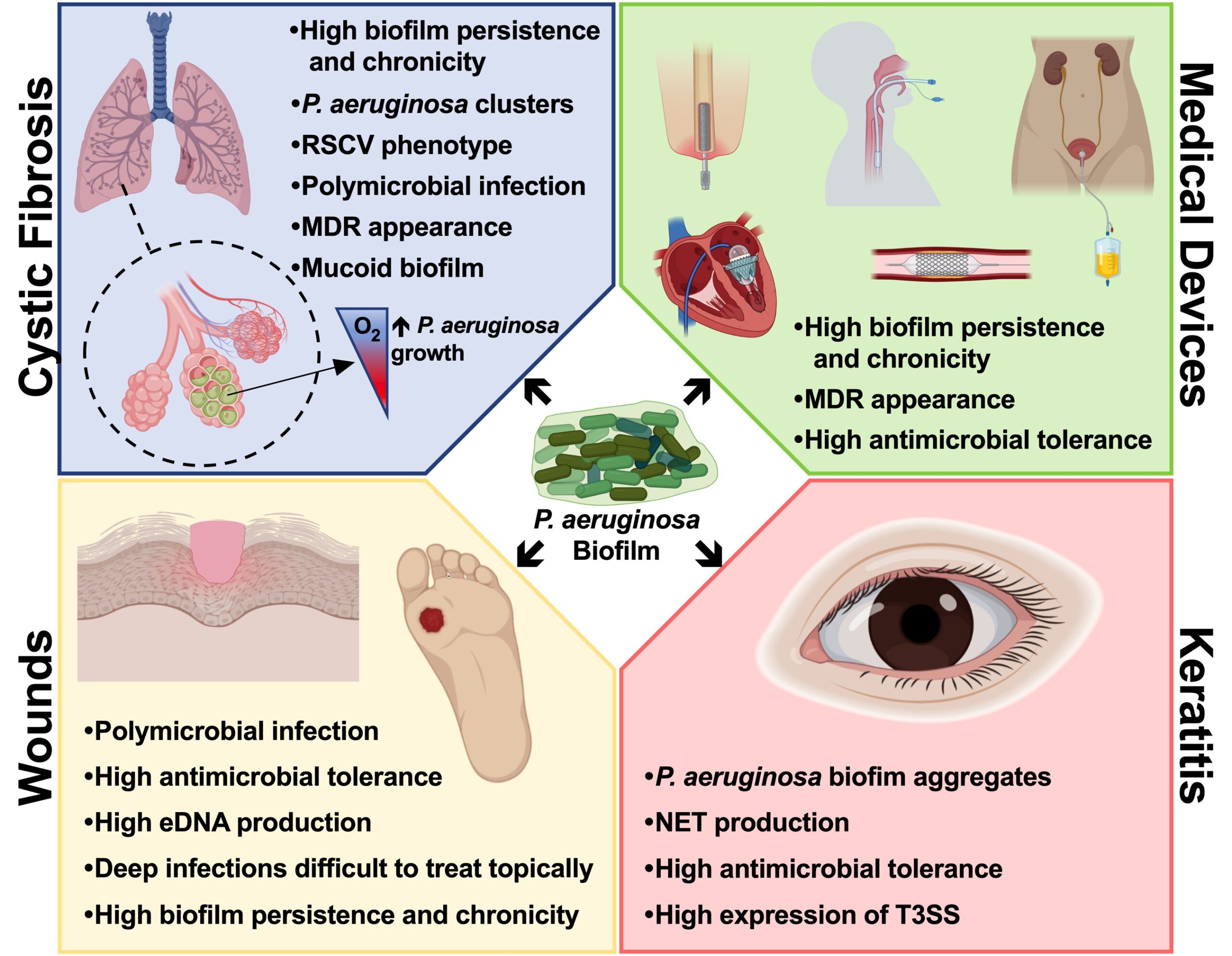
Over 60% of all human infections are characterized by the formation of a biofilm, which is involved in a wide variety of pathological conditions by either growing over human tissues (Cystic Fibrosis, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, chronic wound, etc.) or by developing on the surfaces of medical devices (e.g. endotracheal tubes, intravenous and urinary catheters, etc.).
Our lab aims to investigate new antimicrobial therapies and strategies to combat bacterial infections with different objectives:
- The use of nanomedicine techniques for the development of novel and specific nanoparticles to deliver existing antibiotics or new identify antimicrobial drugs, significantly when the bacteria are growing in biofilm, close to the physiological conditions of the disease and where the current chemotherapy fails;
- The identification and screening of new molecules for the highly selective inhibition of new antibacterial targets (e.g. ribonucleotide reductases);
- The use of nanomedicine techniques for the development of novel and specific nanoparticles to deliver existing antibiotics or new identify antimicrobial drugs, significantly when the bacteria are growing in biofilm, close to the physiological conditions of the disease and where the current chemotherapy fails;
- To study new methodologies to treat chronic bacterial infections in patients suffering cystic fibrosis;
- To develop a new family of antibacterial vaccines;
- The development of new strategies for bacterial coculture systems;
- To study and develop models for wound healing infections and the search of novel treatments;
- The use of lab-on-a-chip technology to deeply elucidate mechanisms to combat bacterial forming biofilm as well as new approaches to identify multiresistant bacteria to different antibiotics.
- To establish the molecular basis for the regulation of genes involved in DNA synthesis (ribonucleotide reductase genes), their importance in virulence and biofilm formation;
We believe these projects will be beneficial to society since we explore the use of different bioengineering approaches to elucidate ways to diagnose and eradicate multi-drug resistant bacteria.
Related links:
Staff
Former Members
Maria del Mar Cendra | PhD Student
Projects
| NATIONAL PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| InfectTreat · Understanding DNA metabolism and new insights in polymicrobial biofilms: development of more efficient therapies to tackle bacterial infections (2022 – 2025) | MICIU. Generación Conocimiento proyectos I+D | Eduard Torrents |
| DISnanoAMR · Desarrollo de nuevas estrategias para hacer frente a la resistencia antibiótica (2022 – 2025) | MICIU. Poryectos de I+D+i en líneas estratégicas | Eduard Torrents |
| IVD-Biofilm · Desarrollo de un nuevo dispositivo para el diagnóstico personalizado en infecciones relacionadas con biopelículas (2022 – 2024) | MICIU. Proyectos Pruebas de Concepto | Eduard Torrents |
| Acuerdo de colaboración ente el IBEC y la Asociación Catalana de Fibrosis Quística (2019 – 2024) | Asociación Catalana de Fibrosis Quística | Eduard Torrents |
| Las biopelículas polimicrobianas para el desarrollo de terapias más eficientes contra las infecciones bacterianas” (2021-2022) | Diputació de Barcelona | Eduard Torrents |
| combatRNR · Comprender la síntesis del ADN en patógenos bacterianos: nuevas estrategias para el tratamiento de enfermedades infecciosas (2019 – 2022) | MICIU. Retos investigación: Proyectos I+D | Eduard Torrents |
| BIOVAC · Artificial bacteria: a novel generation of bioinspired vaccines (2020 – 2023) | BIST. BIST Ignite Program | Eduard Torrents |
| Las biopelículas polimicrobianas para el desarrollo de terapias más eficientes contra las infecciones bacterianas” (2021-2022) | Diputació de Barcelona | Eduard Torrents |
| FINISHED PROJECTS | FINANCER | PI |
|---|---|---|
| Terapias alternativas para el tratamiento de las infecciones bacterianas crónicas en pacientes con fibrosis quística a (2019-2021) | Asociación Catalana de Fibrosis Quística | Eduard Torrents |
| Noves estratègies antimicrobianes per combatre la fibrosi quística (2016-2020) | Obra Social La Caixa | Eduard Torrents |
| BiofilmChip CaixaImpulse BiofilmChip (2018 – 2020) | Obra Social La Caixa | Eduard Torrents |
| Desarrollo de una nueva familia de compuestos antimicrobianos | Asociación Catalana de Fibrosis Quística | Eduard Torrents |
| Identificación y administración de nuevas moléculas antimicrobianas contra Pseudomonas aeruginosa creciendo en biofilm | Asociación Española Fibrosis Quística, Becas de Investigación “Pablo Motos” | Eduard Torrents |
| Novel strategies to combat bacterial chronic infections by the development of microfluidics platforms to analyse and treat bacterial growing in biofilms (2016) | Obra Social La Caixa | Eduard Torrents |
| Redes reguladoras de la expresión génica de las distintas ribonucleotidil reductasas en bacterias | MINECO, I+D-Investigación fundamental no orientada | Eduard Torrents |
| BACTSHOT Novel antimicrobial therapy (2016-2017) | EIT Health Head Start – Proof of Concept | Eduard Torrents |
| inhibitRNR Las ribonucleotido reductasas como una nueva diana terapéutica frente a patógenos bacterianos (2016-2018) | MINECO, Retos investigación: Proyectos I+D | Eduard Torrents |
| Ribonucleotide reductasas: una nueva diana terapéutica contra organismos patógenos en enfermos de fibrosis quística (2010-2017) | Asociación Española Fibrosis Quística, Becas de Investigación “Pablo Motos” | Eduard Torrents |
| RNRbiotic New strategy to combat bacterial infections (2015-2017) | Obra Social La Caixa, Caixaimpulse | Eduard Torrents |
Publications
(See full publication list in ORCID)
Check for more detailed information on the outputs of the Group at IBEC CRIS portal.
Publications list:
Equipment
- Zeiss LSM 800 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
- Nikon Inverted Fluorescent microscope ECLIPSE Ti-S/L100
- Cell culture facilities for microbial infections
- Characterization of nanoparticles/biomaterial antibacterial activity
- Drosophila melanogaster and Galleria mellonella as a model host for bacterial infections
- Continuous flow system model for bacterial biofilm development
- Single Channel Fiber-Optic Oxygen Meter with microsensor
- Molecular biology, biochemistry and protein purification facilities
- Bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production
Collaborations
- Prof. Daniel Ruiz
Català de Nanociència i Nanotecnologia (ICN2), Barcelona, Spain - Prof. Bianca Sclavi
NRS Biologie Computationnelle et Quantitative. Sobornne Université. Paris. France - Dr. Esther Julián
Dept. de Genètica i de Microbiologia, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Spain - Prof. Josep Samitier
IBEC - Prof. Santiago Vazquez
Laboratori de química farmacèutica, Pharmacy Faculty, Barcelona University - Prof. Gabriel Gomila
IBEC - Dr. Maarten Fauvart
IMEC, Leuven, Belgium
News

New insights into how bacteria control DNA synthesis open the door to next‑generation antimicrobials
A study led by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and the Molecular Biology Institute of Barcelona (IBMB) provides the most detailed picture to date of NrdR — the master regulator of ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) in bacteria. Researchers obtained the first detailed images of the complete NrdR protein structure and showed how changes in the shape and grouping of this protein affect the way it controls key processes inside the cell. The findings, recently published in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, increase our understanding of how bacteria regulate the production of the molecular building blocks of DNA, a crucial aspect for both fundamental microbiology and the development of new antimicrobial strategies.

Berlin Hosts the Mid-Term Meeting and First Workshop of the SPM4.0 Network coordinated by IBEC
The SPM4.0 consortium convened at Charité–Berlin for its first training workshop and mid-term meeting, reinforcing scientific collaboration and supporting the development of the project’s doctoral researchers. The sessions offered a comprehensive overview of ongoing scientific progress and future training activities. This milestone moment further strengthened coordination across the network and set the pace for upcoming project objectives.

Bioengineering for precision medicine at the 18th IBEC Symposium
The 18th annual IBEC Symposium focused on ‘Bioengineering for Precision Medicine’, which is one of IBEC’s key areas of application. The event was attended by nearly 300 people, including local and international researchers. The multidisciplinary environment provided experts from other centres and the IBEC community with the opportunity to present their projects and exchange knowledge.

Seven additional IBEC labs achieve top-level in My Green Lab certification
Seven more research groups at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have been certified by My Green Lab, reaching the highest rating, the Green Level, for sustainable laboratory practices. With these additions, IBEC core facilities and 70% of the Institute’s laboratories are now certified.
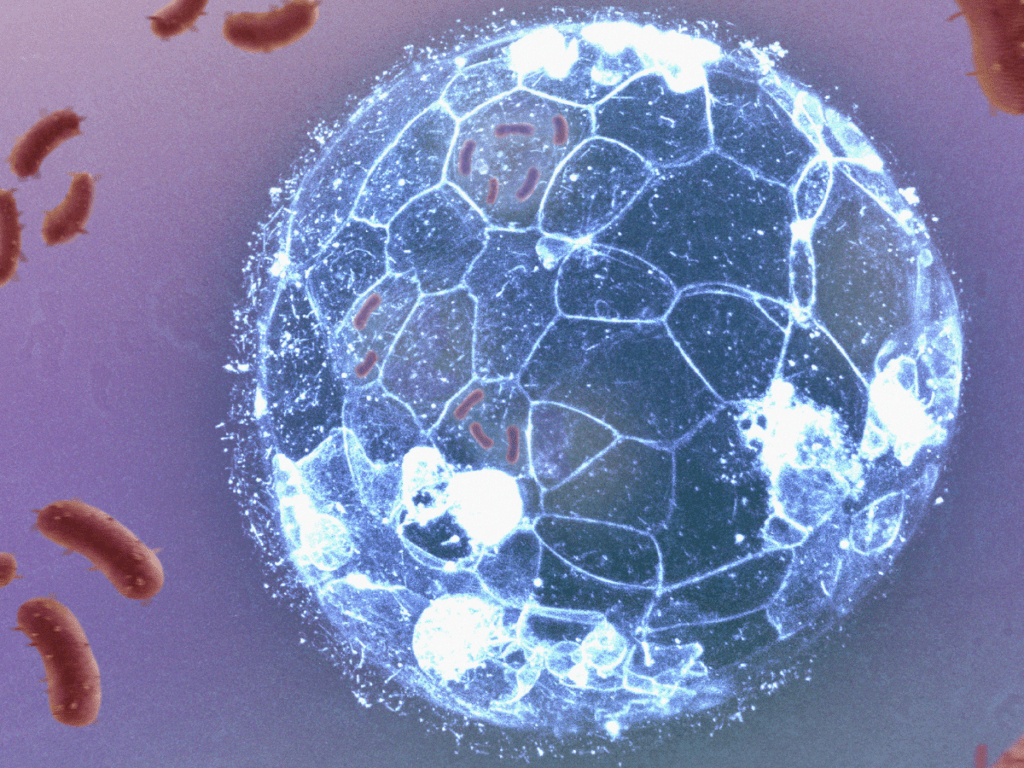
Embryos can eliminate bacterial infections before forming their immune system, a new research shows
The work, led by a team from the CSIC and IDIBELL, with the collaboration of IBEC, manages to visualise how embryonic cells eliminate bacterial infections, before the formation of the immune system. The research describes a mechanism of phagocytosis similar to that used by white blood cells, and reveals that this mechanism is also present in human embryos.
Common lung bacteria team up to evade immune defences
A study led by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) has uncovered how co-infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Mycobacterium abscessus, two common lung pathogens, can suppress immune responses and worsen outcomes in patients with respiratory diseases. The findings, published today in the journal Virulence, provide new insight into why polymicrobial infections are particularly difficult to treat and open the door to new therapeutic strategies.
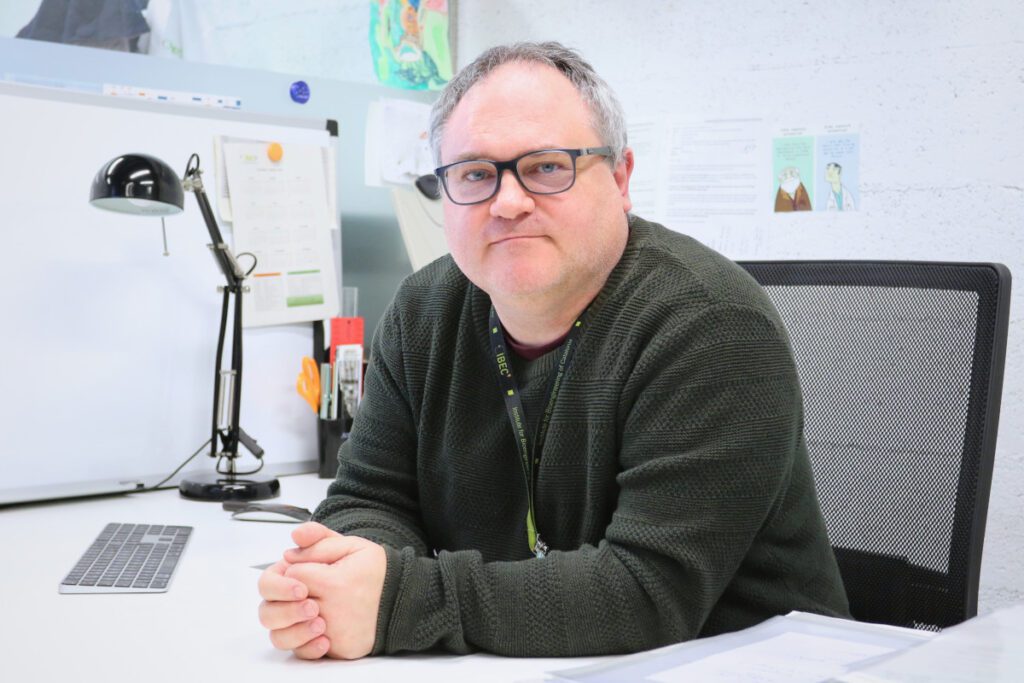

Eduard Torrents receives the ICREA Academia programme distinction
IBEC researcher Eduard Torrents has been awarded the ICREA Academia distinction by the Catalan Institute for Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA). The head of IBEC’s Bacterial Infections: Antimicrobial Therapies group received the award in the Life and Health Sciences category.
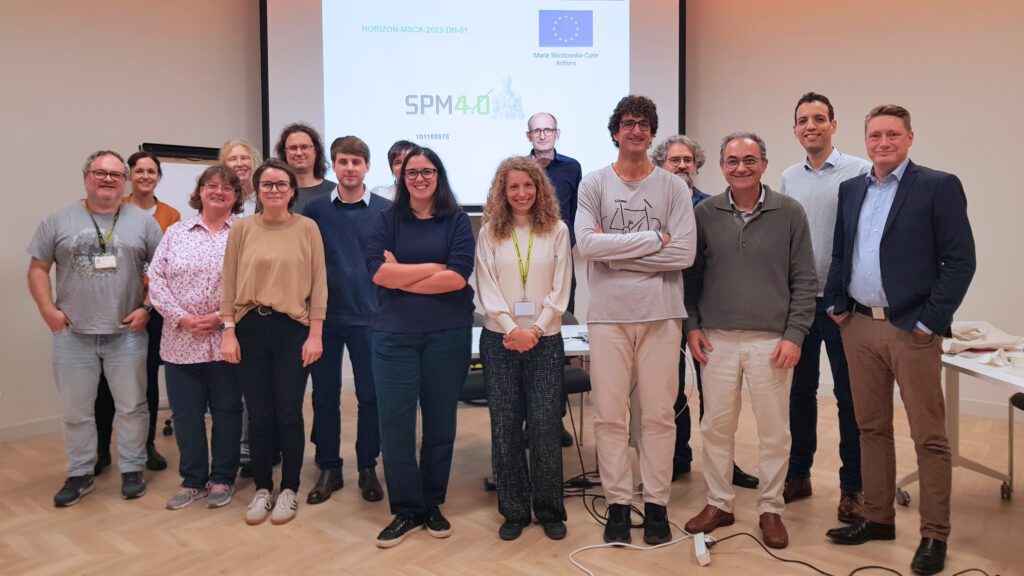

IBEC hosts the EU Project SPM4.0 kick-off meeting
Researchers from across Europe gathered for the kick-off meeting of the SPM4.0 project, an innovative Marie Curie Skłodowska Doctoral Network (MSCA-DN) dedicated to advancing the capabilities of autonomous Scanning Probe … Read more

IBEC and VHIR hold a collaboration day to promote synergies
The 1st Translational Collaboration Day between the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Research (VHIR) and the Institute of Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), held on 21st November, was an opportunity to learn about the projects and research lines of both institutions and to promote interaction between professionals.

Histones against bacterial infections
Research led by IBEC has analysed the antimicrobial activity of human histones against various bacteria, both in solution and in biofilm. The results are very promising and open the door to finding new, more effective treatments, particularly against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. This bacterium is mainly responsible for the development of chronic wounds and lung failure in patients with cystic fibrosis and other respiratory diseases.
Jobs
Senior Technician at the Bacterial Infections and Antimicrobial Therapy (BIAT) Research Group
Ref: ST-ET // Deadline: 23/09/2025
Laboratory technician at the Bacterial Infections and Antimicrobial Therapy (BIAT) Research Group
Introduction to the vacant position: The Bacterial Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy Group is looking for a Laboratory Technician to work on the development of new technologies to treat chronic bacterial … Read more
Post-Doctoral position at the Bacterial Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy (BIAT) Research Group (PD_ET)
Ref: PD_ET // Deadline: 24/01/2024
Postdoctoral position at the Bacterial Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy (BIAT) Research Group (Pd_ET)
Ref: Pd_ET // Deadline: 07/07/2023
Postdoctoral position at the Bacterial Infection and Antimicrobial Therapy (BIAT) Research Group
Ref: BIAT // Deadline: 28/02/2023


 ibecbarcelona.eu
ibecbarcelona.eu