Identified a new repairing mechanism of the peripheral nervous system by applyting bioengineering techniques
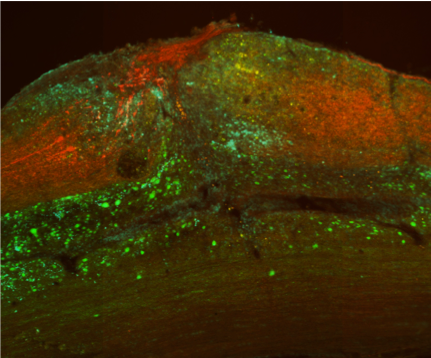
 The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
Thanks to this research they have discovered that muscle activity can activate the neurons and accelerate their regeneration after an injury.


 The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
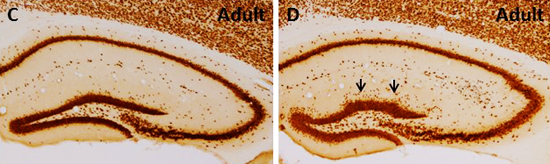
 José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells.
José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells.