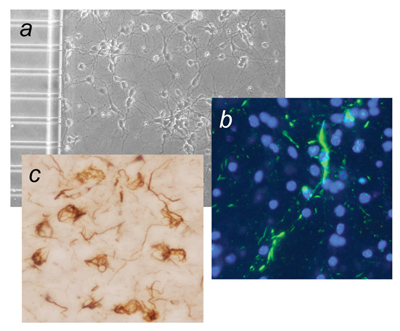
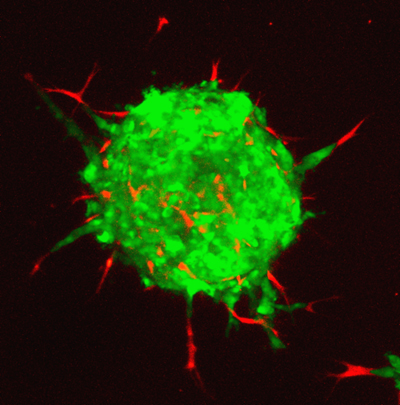
IBEC research features in ChemComm’s “Emerging Investigators” issue
IBEC junior group leader Lorenzo Albertazzi is a contributor to the 2017 edition of ChemComm Emerging Investigators, which is published annually by the UK’s Royal Society of Chemistry.
Now in its seventh year, the special issue showcases research carried out by internationally recognised, up-and-coming scientists in the early stages of their independent careers, and who are making outstanding contributions to their respective fields.



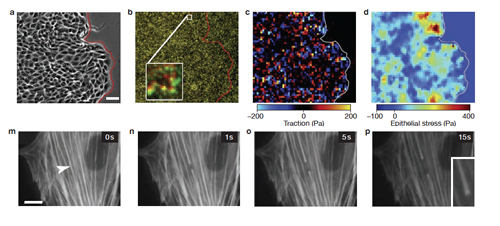
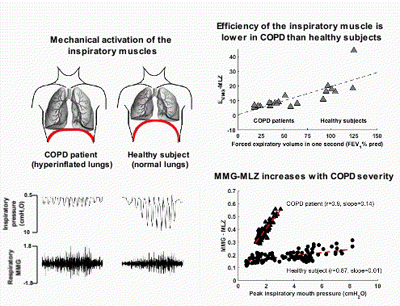
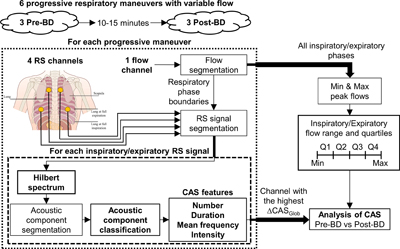
 Some research published in PLOS ONE represents a new step towards translating IBEC’s basic research – specifically the novel signal processing and interpretation algorithms developed by Raimon Jané’s group – to clinical applications in hospitals.
Some research published in PLOS ONE represents a new step towards translating IBEC’s basic research – specifically the novel signal processing and interpretation algorithms developed by Raimon Jané’s group – to clinical applications in hospitals.