Research news
A new method confirms the impact of COVID-19 confinement measures on mental health and well-being
Researchers from the SPECS lab at IBEC develop a new method to evaluate the mental health and wellbeing of people living under strict confinement measures such those during COVID-19 pandemic on April 2020. The study, conducted with people living in 17 countries, confirms that confinement measurements leads to a negative impact on the emotional wellbeing. The researchers also detected some personal situations that can entail a higher risk for the mental health and wellbeing.
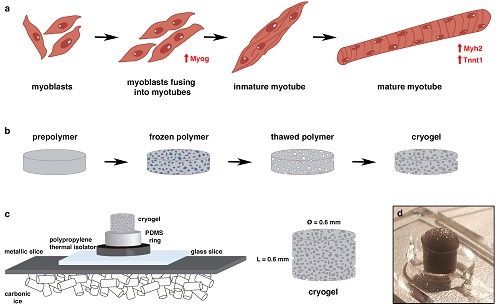
Nanotechnology to improve human tissue growth in the laboratory
 Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have developed an innovative scaffold that allows muscle tissues growth at the millimetre scale in the laboratory.
Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have developed an innovative scaffold that allows muscle tissues growth at the millimetre scale in the laboratory.
This technology opens the door to potential applications in fields such as organ transplantation and engineering, drug screening and disease modelling.
Researchers identify a mechanism that explains the recurrence of many lung infections
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has discovered that strains of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients are more persistent than laboratory strains and propose a molecular mechanism to explain intracellular survival.
The study, published in the journal Virulence, finds that the class II ribonucleotide reductase enzyme (RNR) plays a key role in frequent lung infections, for example, those that occur in patients with cystic fibrosis.
New avenues for identifying and evaluating treatments for CDKL5 deficiency disorder
 Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study led by Imperial College London in which the role of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDKL5) in pain perception has been uncovered.
Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study led by Imperial College London in which the role of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDKL5) in pain perception has been uncovered.
The defective version of the gene that produces this protein is behind CDKL5 deficiency disorder, a rare disease with no cure for which effective treatments will now be testable in mouse model, thanks to the results of this work.
New biodegradable nanomotors for biomedical applications
A paper published in Nano Letters describes the engineering and functionality of a biocompatible and biodegradable nanomotor. This hybrid structure, which is composed of an organic exterior, propels itself using inorganic nanoparticles acting as an engine that the researchers have synthesized inside the nanomotor.
The research was led by Jan van Hest and Laoi Abdelmohsen from the Institute of Complex Molecular Systems at TU/e in collaboration with Samuel Sánchez from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in Barcelona, as well as researchers based in China and the UK.
Artificial Intelligence tools to advance in the research and development of biomaterials
 Experts in bioengineering and informatics, including IBEC´s Associated Researcher Maria-Pau Ginebra, have published a paper where the researchers propose the creation of tools based on Artificial Intelligence for the development of biomaterials in Nature Reviews Materials.
Experts in bioengineering and informatics, including IBEC´s Associated Researcher Maria-Pau Ginebra, have published a paper where the researchers propose the creation of tools based on Artificial Intelligence for the development of biomaterials in Nature Reviews Materials.
Nature Reviews Materials journal has published an article signed by scientists from the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) outlining the great possibilities that artificial intelligence offers towards the progress in the design and development of biomaterials.
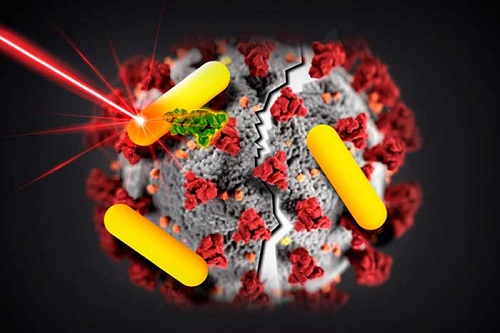
Bioengineering against the most resistant and deadly bacterial infections
 An international team, led by Profs Giuseppe Battaglia and Loris Rizzello from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), carried out out a study that opens the door to a new therapy capable of quickly and effectively eliminating infections caused by intracellular bacteria, the most resistant to immune defenses.
An international team, led by Profs Giuseppe Battaglia and Loris Rizzello from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), carried out out a study that opens the door to a new therapy capable of quickly and effectively eliminating infections caused by intracellular bacteria, the most resistant to immune defenses.
This therapy, based on synthetic vesicles, could considerably reduce the dose and duration of antimicrobial treatments, thus reducing the danger of generating resistance to antibiotics of pathogens such as those leading to tuberculosis.
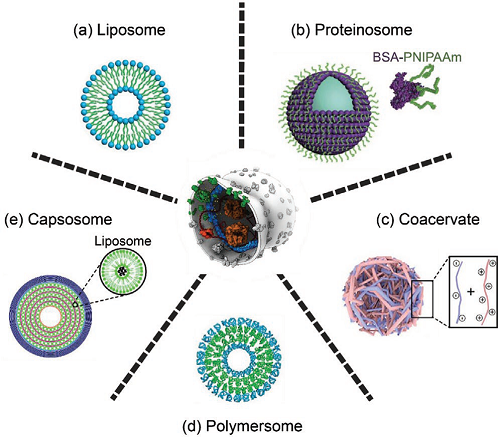
Artificial systems imitate how cells move and communicate
A review published in the scientific journal Small elegantly summarises the most important cellular biomimicry research of the past few years on synthetic soft-architectures, with a view to inspiring future developments in the field.
Samuel Sánchez, Group Leader at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) co-authored this piece, alongside world-renowned experts in bioengineering and cell synthesis.
Nanoparticles and supercomputers against SARS-CoV-2
The research group at the UPC, led by the IBEC Associated Researcher Carlos Aleman, will investigate in collaboration with the company B. Braun, the detection, blocking and elimination of the SARS-CoV-2 virus by using functionalized nanoparticles and activation of nano-sources of heat.
To carry out the investigation, they will be allowed to use the supercomputer installed in France.


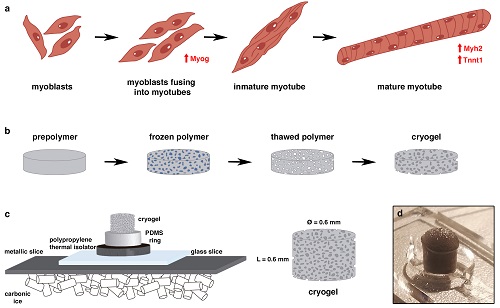 Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have developed an innovative scaffold that allows muscle tissues growth at the millimetre scale in the laboratory.
Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have developed an innovative scaffold that allows muscle tissues growth at the millimetre scale in the laboratory.

 Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study led by Imperial College London in which the role of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDKL5) in pain perception has been uncovered.
Researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have participated in a study led by Imperial College London in which the role of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDKL5) in pain perception has been uncovered.
 Experts in bioengineering and informatics, including IBEC´s Associated Researcher Maria-Pau Ginebra, have published a paper where the researchers propose the creation of tools based on Artificial Intelligence for the development of biomaterials in Nature Reviews Materials.
Experts in bioengineering and informatics, including IBEC´s Associated Researcher Maria-Pau Ginebra, have published a paper where the researchers propose the creation of tools based on Artificial Intelligence for the development of biomaterials in Nature Reviews Materials.
 An international team, led by Profs Giuseppe Battaglia and Loris Rizzello from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), carried out out a study that opens the door to a new therapy capable of quickly and effectively eliminating infections caused by intracellular bacteria, the most resistant to immune defenses.
An international team, led by Profs Giuseppe Battaglia and Loris Rizzello from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), carried out out a study that opens the door to a new therapy capable of quickly and effectively eliminating infections caused by intracellular bacteria, the most resistant to immune defenses.