Researchers at IBEC provide new insights on how to treat chronic infections
Researchers at Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) have managed to recreate the coculture conditions and environmental requisites that would allow the simultaneous and stable growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, two major pathogens commonly found growing together in intricate biofilms in disease-affected lungs or wounds.
Most chronic infections occur due to the inherent capacity of some bacterial pathogens to grow in biofilms. Biofilm-associated infections, which have become a critical worldwide threat, have historically been treated as single-species events.



 The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
The Molecular and cellular neurobiotechnology group with the collaboration of the Nanobioengineering group, both of them at IBEC, have applied a new light-stimulated technique to modulate muscular activity and stimulate cell regeneration of the peripheral nervous system.
 José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells.
José Antonio del Río, principal investigator at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) together with Dr. Isidre Ferrer from Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) led a study where they have unraveled that the pathology shown by patients with Globular Glial Tauopathy is due to the generation of harmful protein deposits for neurons and glial cells. 

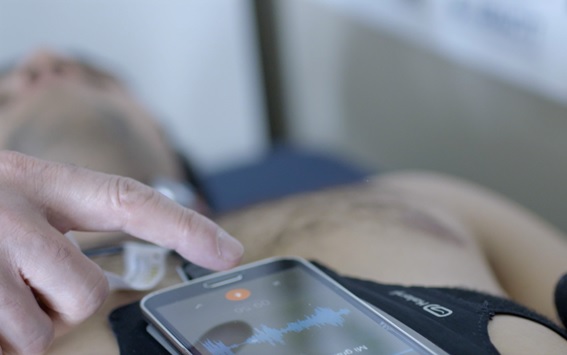
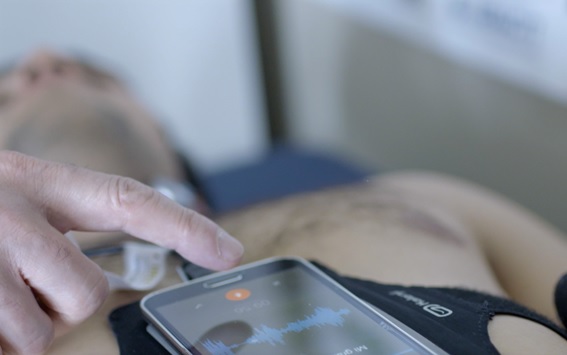 The Biomedical signal processing and interpretation group at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed a portable, cheap and non-invasive system to detect obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) at home, a disorder characterized by recurrent airflow cessation during sleep. Researchers propose a novel method consisting of analyzing acoustic signals recorded with a smartphone.
The Biomedical signal processing and interpretation group at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed a portable, cheap and non-invasive system to detect obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) at home, a disorder characterized by recurrent airflow cessation during sleep. Researchers propose a novel method consisting of analyzing acoustic signals recorded with a smartphone.