An optogenetic tool that directs cellular contractility using light
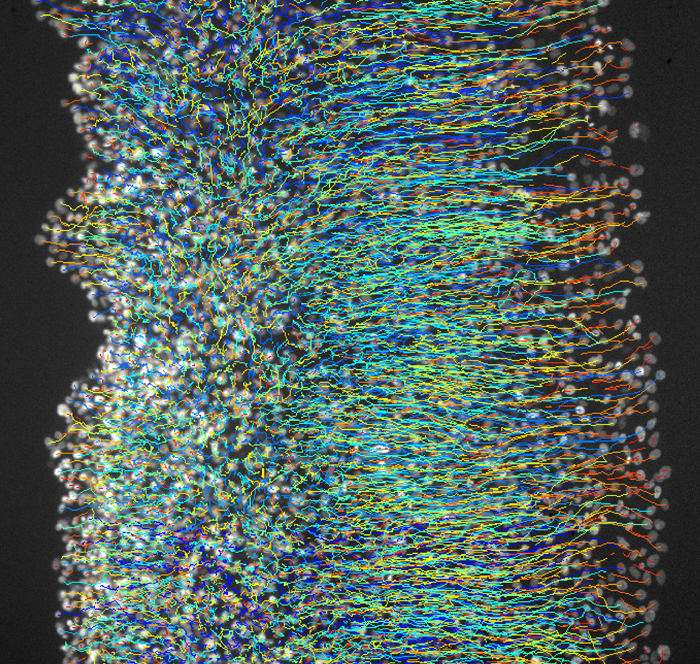
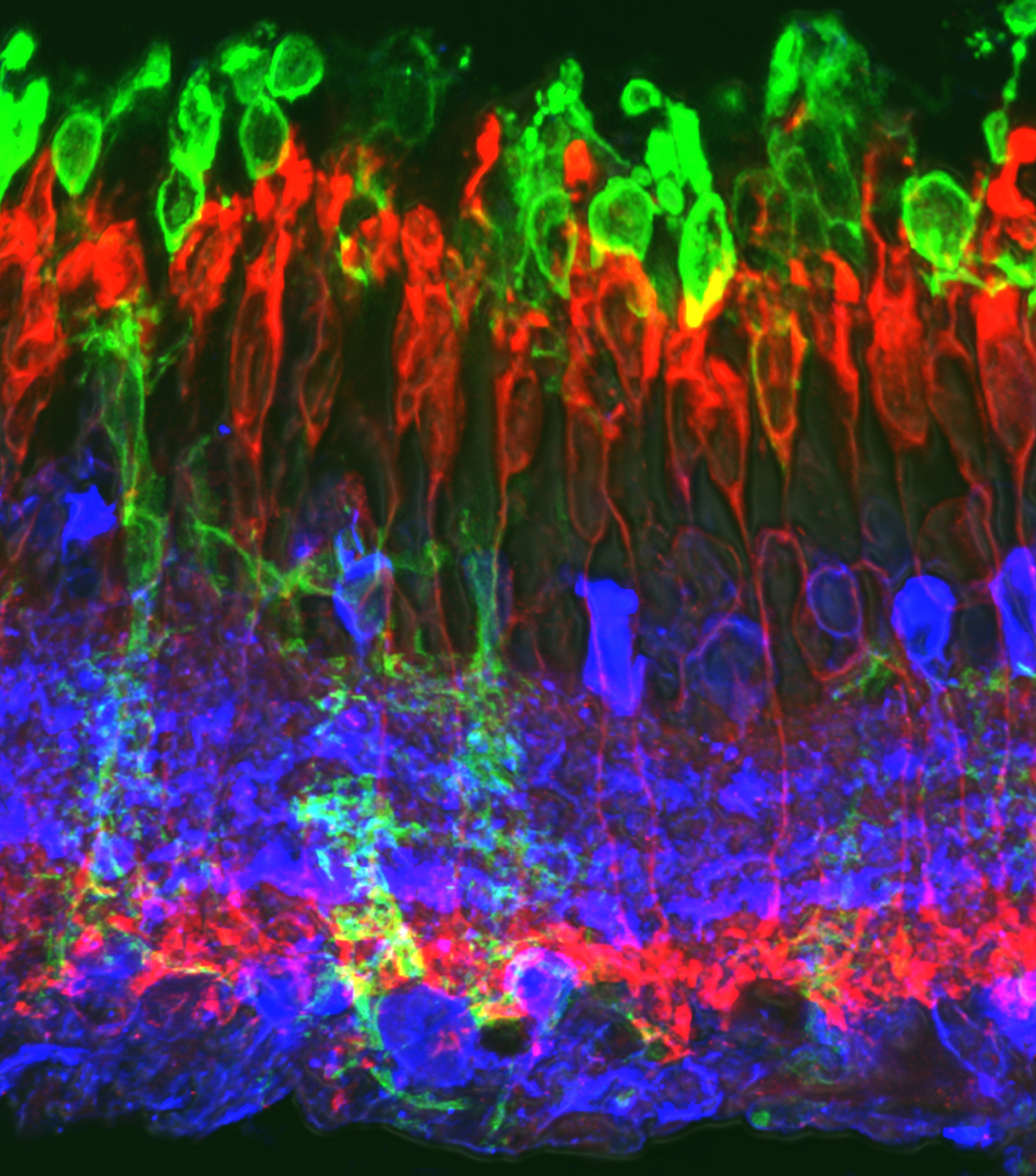
 Researchers at IBEC have controlled the contractility of a group of epithelial cells using an optogenetic switch activated by light.
Researchers at IBEC have controlled the contractility of a group of epithelial cells using an optogenetic switch activated by light.
The study, published in Nature Communications, explains how this novel technique allows for rapid, local and reversible changes in the forces exerted by cells, as well as tissue contraction.

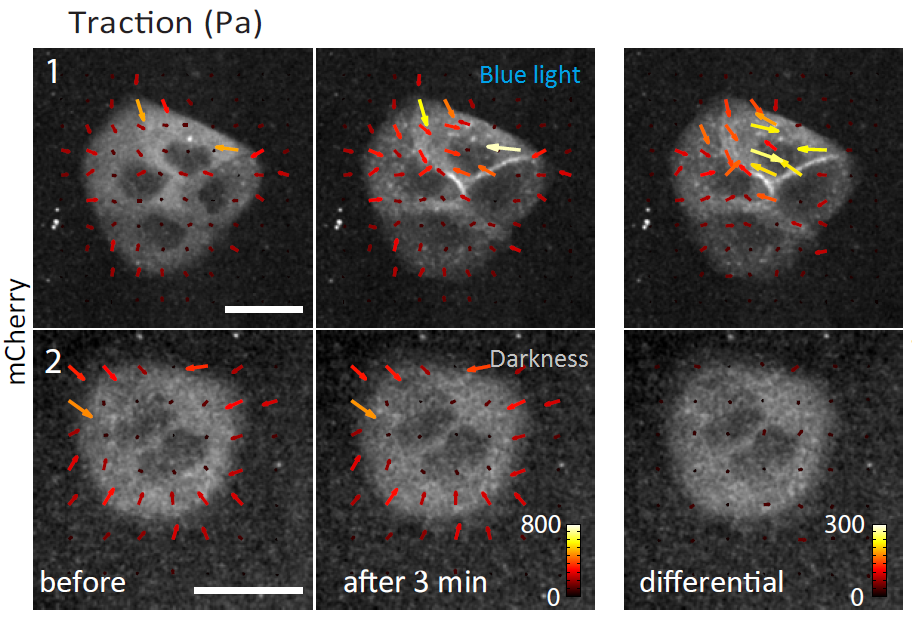
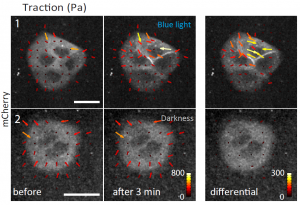 Researchers at IBEC have controlled the contractility of a group of epithelial cells using an optogenetic switch activated by light.
Researchers at IBEC have controlled the contractility of a group of epithelial cells using an optogenetic switch activated by light.