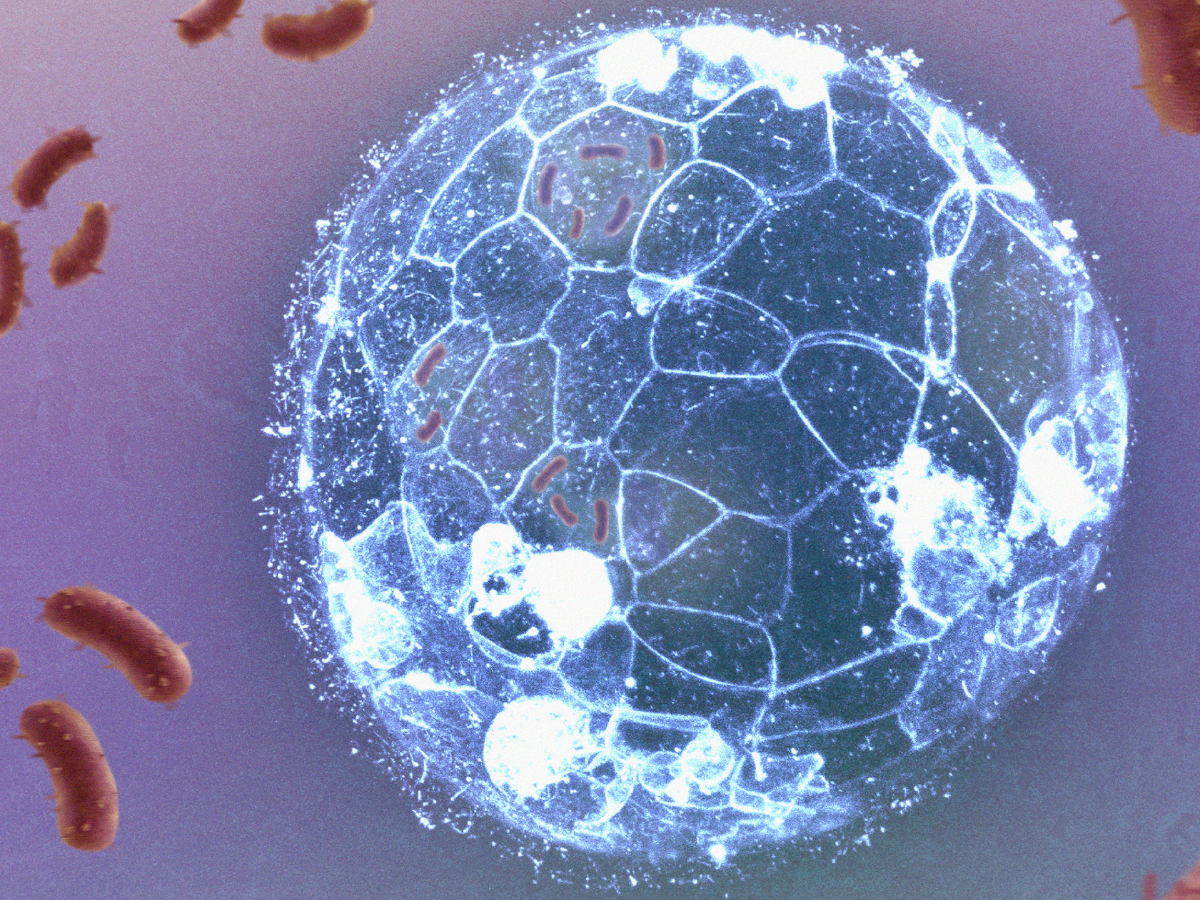
Embryos can eliminate bacterial infections before forming their immune system, a new research shows
The work, led by a team from the CSIC and IDIBELL, with the collaboration of IBEC, manages to visualise how embryonic cells eliminate bacterial infections, before the formation of the immune system. The research describes a mechanism of phagocytosis similar to that used by white blood cells, and reveals that this mechanism is also present in human embryos.